Crohn's Disease
OVERVIEW | CAUSES | RISK FACTORS | SYMPTOMS | COMPLICATION | Diagnosis | TREATMENT | PREVENTION | REFERENCES
Overview
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It causes inflammation of your digestive tract, which can lead to abdominal pain, severe diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss and malnutrition.
Inflammation caused by Crohn's disease can involve different areas of the digestive tract in different people. This inflammation often spreads into the deeper layers of the bowel.
Crohn's disease can be both painful and debilitating, and sometimes may lead to life-threatening complications.
While there's no known cure for Crohn's disease, therapies can greatly reduce its signs and symptoms and even bring about long-term remission and healing of inflammation. With treatment, many people with Crohn's disease are able to function well.
Causes
The exact cause of Crohn's disease remains unknown. Previously, diet and stress were suspected, but now doctors know that these factors may aggravate, but don't cause, Crohn's disease. Several factors, such as heredity and a malfunctioning immune system, likely play a role in its development.
- Immune system. It's possible that a virus or bacterium may trigger Crohn's disease; however, scientists have yet to identify such a trigger. When your immune system tries to fight off the invading microorganism, an abnormal immune response causes the immune system to attack the cells in the digestive tract, too.
- Heredity. Crohn's is more common in people who have family members with the disease, so genes may play a role in making people more susceptible. However, most people with Crohn's disease don't have a family history of the disease.
Risk factors
Risk factors for Crohn's disease may include:
- Age. Crohn's disease can occur at any age, but you're likely to develop the condition when you're young. Most people who develop Crohn's disease are diagnosed before they're around 30 years old.
- Ethnicity. Although Crohn's disease can affect any ethnic group, whites have the highest risk, especially people of Eastern European (Ashkenazi) Jewish descent. However, the incidence of Crohn's disease is increasing among Black people who live in North America and the United Kingdom.
- Family history. You're at higher risk if you have a first-degree relative, such as a parent, sibling or child, with the disease. As many as 1 in 5 people with Crohn's disease has a family member with the disease.
- Cigarette smoking. Cigarette smoking is the most important controllable risk factor for developing Crohn's disease. Smoking also leads to more-severe disease and a greater risk of having surgery. If you smoke, it's important to stop.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications. These include ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), naproxen sodium (Aleve), diclofenac sodium and others. While they do not cause Crohn's disease, they can lead to inflammation of the bowel that makes Crohn's disease worse.
Symptoms
In Crohn's disease, any part of your small or large intestine can be involved, and it may be continuous or may involve multiple segments. In some people, the disease is confined to the colon, which is part of the large intestine.
Signs and symptoms of Crohn's disease can range from mild to severe. They usually develop gradually, but sometimes will come on suddenly, without warning. You may also have periods of time when you have no signs or symptoms (remission).
When the disease is active, signs and symptoms may include:
- Diarrhea
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Blood in your stool
- Mouth sores
- Reduced appetite and weight loss
- Pain or drainage near or around the anus due to inflammation from a tunnel into the skin (fistula)
Other signs and symptoms
People with severe Crohn's disease may also experience:
- Inflammation of skin, eyes and joints
- Inflammation of the liver or bile ducts
- Kidney stones
- Iron deficiency (anemia)
- Delayed growth or sexual development, in children
Complications
Crohn's disease may lead to one or more of the following complications:
- Bowel obstruction. Crohn's disease can affect the entire thickness of the intestinal wall. Over time, parts of the bowel can scar and narrow, which may block the flow of digestive contents. You may require surgery to remove the diseased portion of your bowel.
- Ulcers. Chronic inflammation can lead to open sores (ulcers) anywhere in your digestive tract, including your mouth and anus, and in the genital area (perineum).
- Fistulas. Sometimes ulcers can extend completely through the intestinal wall, creating a fistula — an abnormal connection between different body parts. Fistulas can develop between your intestine and your skin, or between your intestine and another organ. Fistulas near or around the anal area (perianal) are the most common kind.
When fistulas develop in the abdomen, food may bypass areas of the bowel that are necessary for absorption. Fistulas may form between loops of bowel, in the bladder or vagina, or through the skin, causing continuous drainage of bowel contents to your skin.
In some cases, a fistula may become infected and form an abscess, which can be life-threatening if not treated. - Anal fissure. This is a small tear in the tissue that lines the anus or in the skin around the anus where infections can occur. It's often associated with painful bowel movements and may lead to a perianal fistula.
- Malnutrition. Diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramping may make it difficult for you to eat or for your intestine to absorb enough nutrients to keep you nourished. It's also common to develop anemia due to low iron or vitamin B-12 caused by the disease.
- Colon cancer. Having Crohn's disease that affects your colon increases your risk of colon cancer. General colon cancer screening guidelines for people without Crohn's disease call for a colonoscopy every 10 years beginning at age 50. Ask your doctor whether you need to have this test done sooner and more frequently.
- Other health problems. Crohn's disease can cause problems in other parts of the body. Among these problems are anemia, skin disorders, osteoporosis, arthritis, and gallbladder or liver disease.
- Medication risks. Certain Crohn's disease drugs that act by blocking functions of the immune system are associated with a small risk of developing cancers such as lymphoma and skin cancers. They also increase risk of infection.
Corticosteroids can be associated with a risk of osteoporosis, bone fractures, cataracts, glaucoma, diabetes and high blood pressure, among other conditions. Work with your doctor to determine risks and benefits of medications. - Blood clots. Crohn's disease increases the risk of blood clots in veins and arteries.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will likely diagnose Crohn's disease only after ruling out other possible causes for your signs and symptoms. There is no single test to diagnose Crohn's disease.
Your doctor will likely use a combination of tests to help confirm a diagnosis of Crohn's disease, including:
Lab tests
- Blood tests. Your doctor may suggest blood tests to check for anemia, a condition in which there aren't enough red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen to your tissues, or to check for signs of infection.
- Stool studies. You may need to provide a stool sample so that your doctor can test for hidden (occult) blood or organisms, such as parasites, in your stool.
Procedures
- Colonoscopy. This test allows your doctor to view your entire colon and the very end of your ileum (terminal ileum) using a thin, flexible, lighted tube with a camera at the end. During the procedure, your doctor can also take small samples of tissue (biopsy) for laboratory analysis, which may help to make a diagnosis. Clusters of inflammatory cells called granulomas, if present, help essentially confirm the diagnosis of Crohn's.
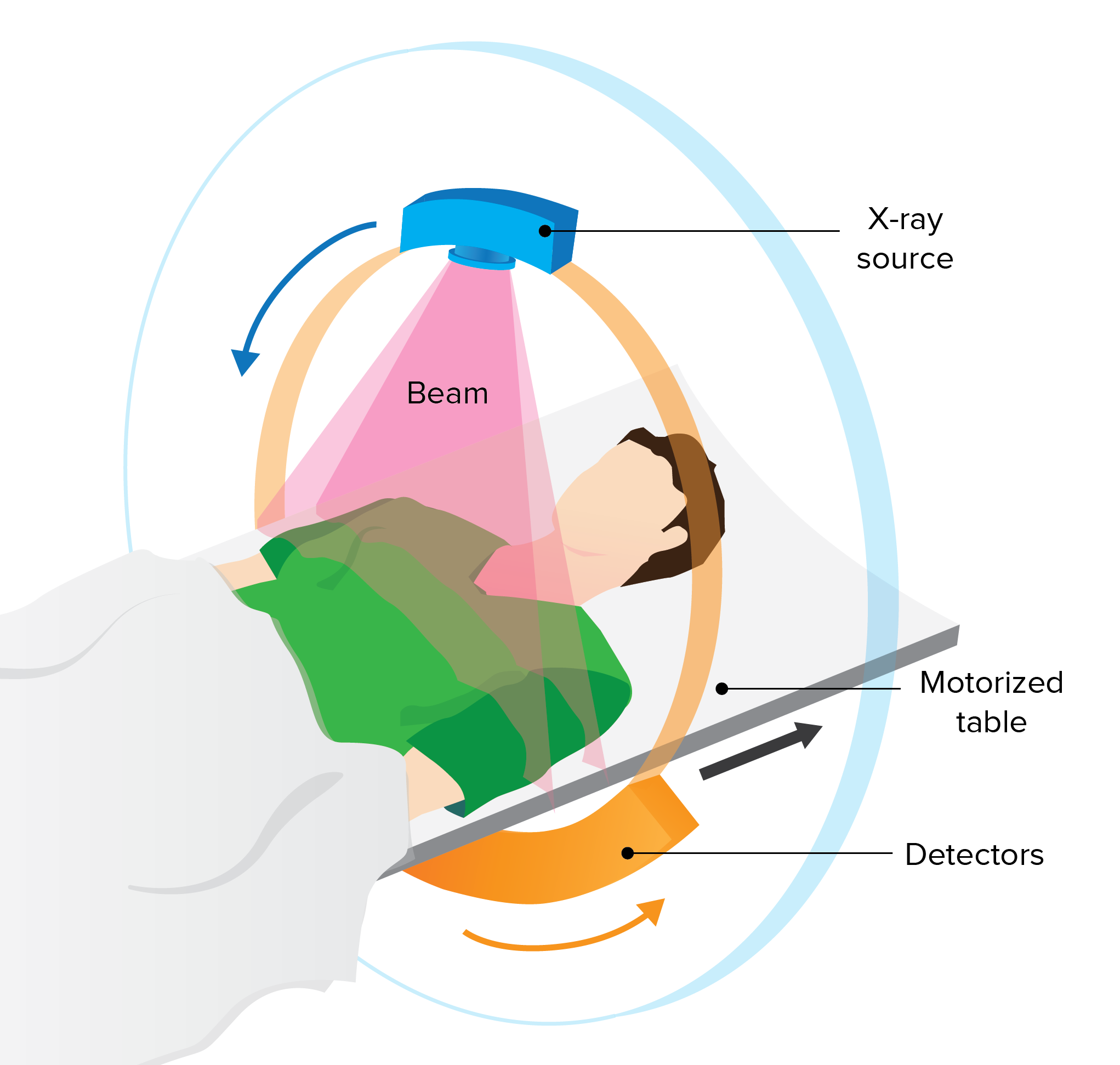
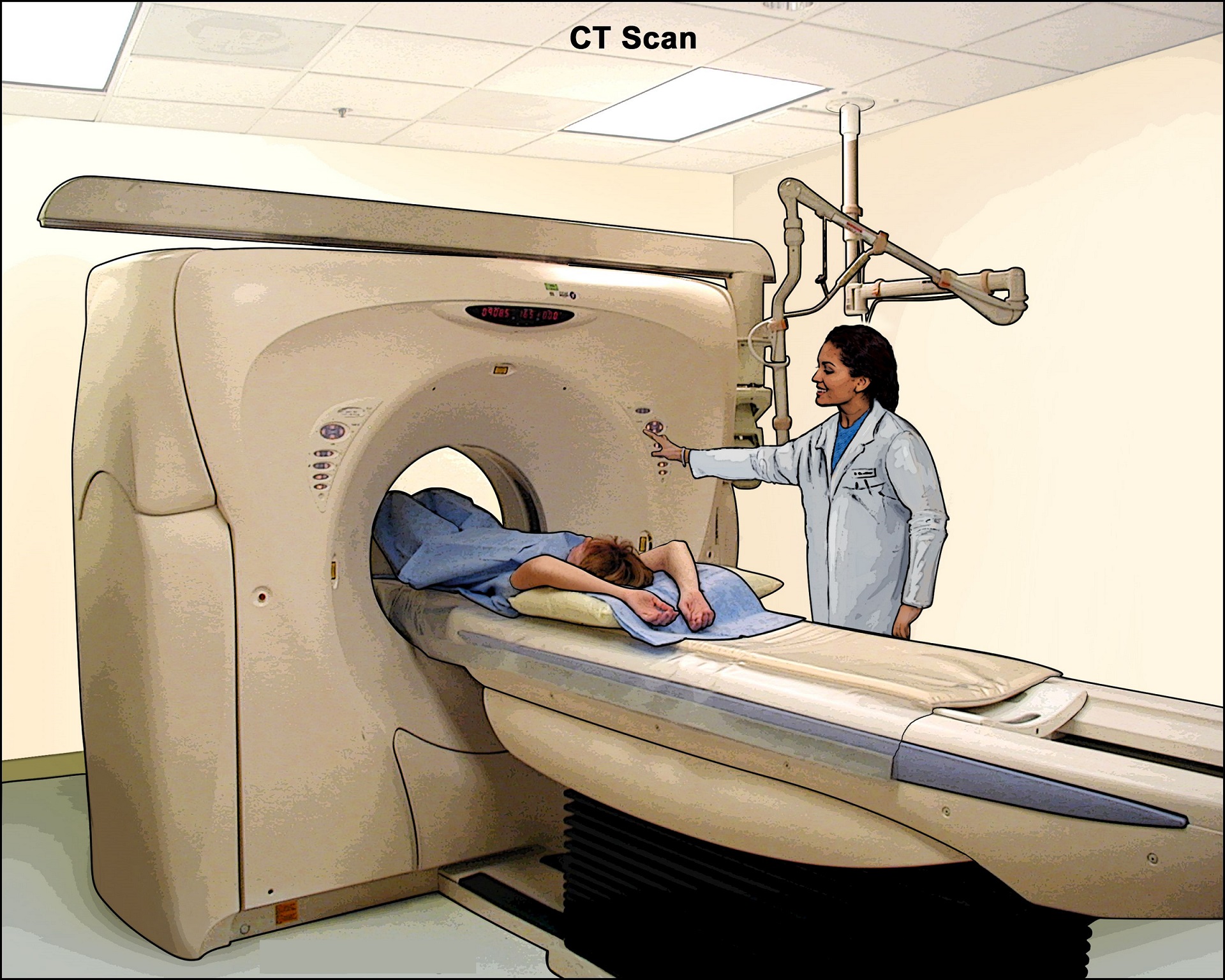
- Computerized tomography (CT). You may have a CT scan — a special X-ray technique that provides more detail than a standard X-ray does. This test looks at the entire bowel as well as at tissues outside the bowel. CT enterography is a special CT scan that provides better images of the small bowel. This test has replaced barium X-rays in many medical centers.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). An MRI scanner uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of organs and tissues. MRI is particularly useful for evaluating a fistula around the anal area (pelvic MRI) or the small intestine (MR enterography).
- Capsule endoscopy. For this test, you swallow a capsule that has a camera in it. The camera takes pictures of your small intestine and transmits them to a recorder you wear on your belt. The images are then downloaded to a computer, displayed on a monitor and checked for signs of Crohn's disease. The camera exits your body painlessly in your stool.
You may still need endoscopy with biopsy to confirm the diagnosis of Crohn's disease. Capsule endoscopy should not be performed if there is a bowel obstruction. - Balloon-assisted enteroscopy. For this test, a scope is used in conjunction with a device called an overtube. This enables the doctor to look further into the small bowel where standard endoscopes don't reach. This technique is useful when capsule endoscopy shows abnormalities but the diagnosis is still in question.
Treatment
There is currently no cure for Crohn's disease, and there is no single treatment that works for everyone. One goal of medical treatment is to reduce the inflammation that triggers your signs and symptoms. Another goal is to improve long-term prognosis by limiting complications. In the best cases, this may lead not only to symptom relief but also to long-term remission.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Anti-inflammatory drugs are often the first step in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. They include:
- Corticosteroids. Corticosteroids such as prednisone and budesonide (Entocort EC) can help reduce inflammation in your body, but they don't work for everyone with Crohn's disease. Doctors generally use them only if you don't respond to other treatments.
Corticosteroids may be used for short-term (three to four months) symptom improvement and to induce remission. Corticosteroids may also be used in combination with an immune system suppressor. - Oral 5-aminosalicylates. These drugs include sulfasalazine (Azulfidine), which contains sulfa, and mesalamine (Asacol HD, Delzicol, others). Oral 5-aminosalicylates have been widely used in the past but now are generally considered of very limited benefit.
Immune system suppressors
These drugs also reduce inflammation, but they target your immune system, which produces the substances that cause inflammation. For some people, a combination of these drugs works better than one drug alone.
Immune system suppressors include:
- Azathioprine (Azasan, Imuran) and mercaptopurine (Purinethol, Purixan). These are the most widely used immunosuppressants for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Taking them requires that you follow up closely with your doctor and have your blood checked regularly to look for side effects, such as a lowered resistance to infection and inflammation of the liver. They may also cause nausea and vomiting.
- Methotrexate (Trexall). This drug is sometimes used for people with Crohn's disease who don't respond well to other medications. You will need to be followed closely for side effects.
Biologics
This class of therapies targets proteins made by the immune system. Types of biologics used to treat Crohn's disease include:
- Natalizumab (Tysabri) and vedolizumab (Entyvio). These drugs work by stopping certain immune cell molecules — integrins — from binding to other cells in your intestinal lining. Because natalizumab is associated with a rare but serious risk of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy — a brain disease that usually leads to death or severe disability — you must be enrolled in a special restricted distribution program to use it.
Vedolizumab recently was approved for Crohn's disease. It works like natalizumab but appears not to carry a risk of brain disease. - Infliximab (Remicade), adalimumab (Humira) and certolizumab pegol (Cimzia). Also known as TNF inhibitors, these drugs work by neutralizing an immune system protein known as tumor necrosis factor (TNF).
- Ustekinumab (Stelara). This was recently approved to treat Crohn's disease by interfering with the action of an interleukin, which is a protein involved in inflammation.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics can reduce the amount of drainage from fistulas and abscesses and sometimes heal them in people with Crohn's disease. Some researchers also think that antibiotics help reduce harmful intestinal bacteria that may play a role in activating the intestinal immune system, leading to inflammation. Frequently prescribed antibiotics include ciprofloxacin (Cipro) and metronidazole (Flagyl).
Other medications
In addition to controlling inflammation, some medications may help relieve your signs and symptoms, but always talk to your doctor before taking any over-the-counter medications. Depending on the severity of your Crohn's disease, your doctor may recommend one or more of the following:
- Anti-diarrheals. A fiber supplement, such as psyllium powder (Metamucil) or methylcellulose (Citrucel), can help relieve mild to moderate diarrhea by adding bulk to your stool. For more severe diarrhea, loperamide (Imodium A-D) may be effective.
- Pain relievers. For mild pain, your doctor may recommend acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) — but not other common pain relievers, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve). These drugs are likely to make your symptoms worse and can make your disease worse as well.
- Vitamins and supplements. If you're not absorbing enough nutrients, your doctor may recommend vitamins and nutritional supplements.
Nutrition therapy
Your doctor may recommend a special diet given by mouth or a feeding tube (enteral nutrition) or nutrients infused into a vein (parenteral nutrition) to treat your Crohn's disease. This can improve your overall nutrition and allow the bowel to rest. Bowel rest can reduce inflammation in the short term.
Your doctor may use nutrition therapy short term and combine it with medications, such as immune system suppressors. Enteral and parenteral nutrition are typically used to get people healthier prior to surgery or when other medications fail to control symptoms.
Your doctor may also recommend a low residue or low-fiber diet to reduce the risk of intestinal blockage if you have a narrowed bowel (stricture). A low residue diet is designed to reduce the size and number of your stools.
Surgery
If diet and lifestyle changes, drug therapy, or other treatments don't relieve your signs and symptoms, your doctor may recommend surgery. Nearly half of those with Crohn's disease will require at least one surgery. However, surgery does not cure Crohn's disease.
During surgery, your surgeon removes a damaged portion of your digestive tract and then reconnects the healthy sections. Surgery may also be used to close fistulas and drain abscesses.
The benefits of surgery for Crohn's disease are usually temporary. The disease often recurs, frequently near the reconnected tissue. The best approach is to follow surgery with medication to minimize the risk of recurrence.
Prevention
There’s no way to prevent Crohn’s disease. These healthy lifestyle changes can ease symptoms and reduce flare-ups:
- Stop smoking.
- Eat a healthy, low-fat diet.
- Exercise regularly.
- Manage stress.