Post- Cholecystectomy Syndrome
OVERVIEW | CAUSES | RISK FACTORS | SYMPTOMS | TREATMENT | PREVENTION | REFERENCES

OVERVIEW
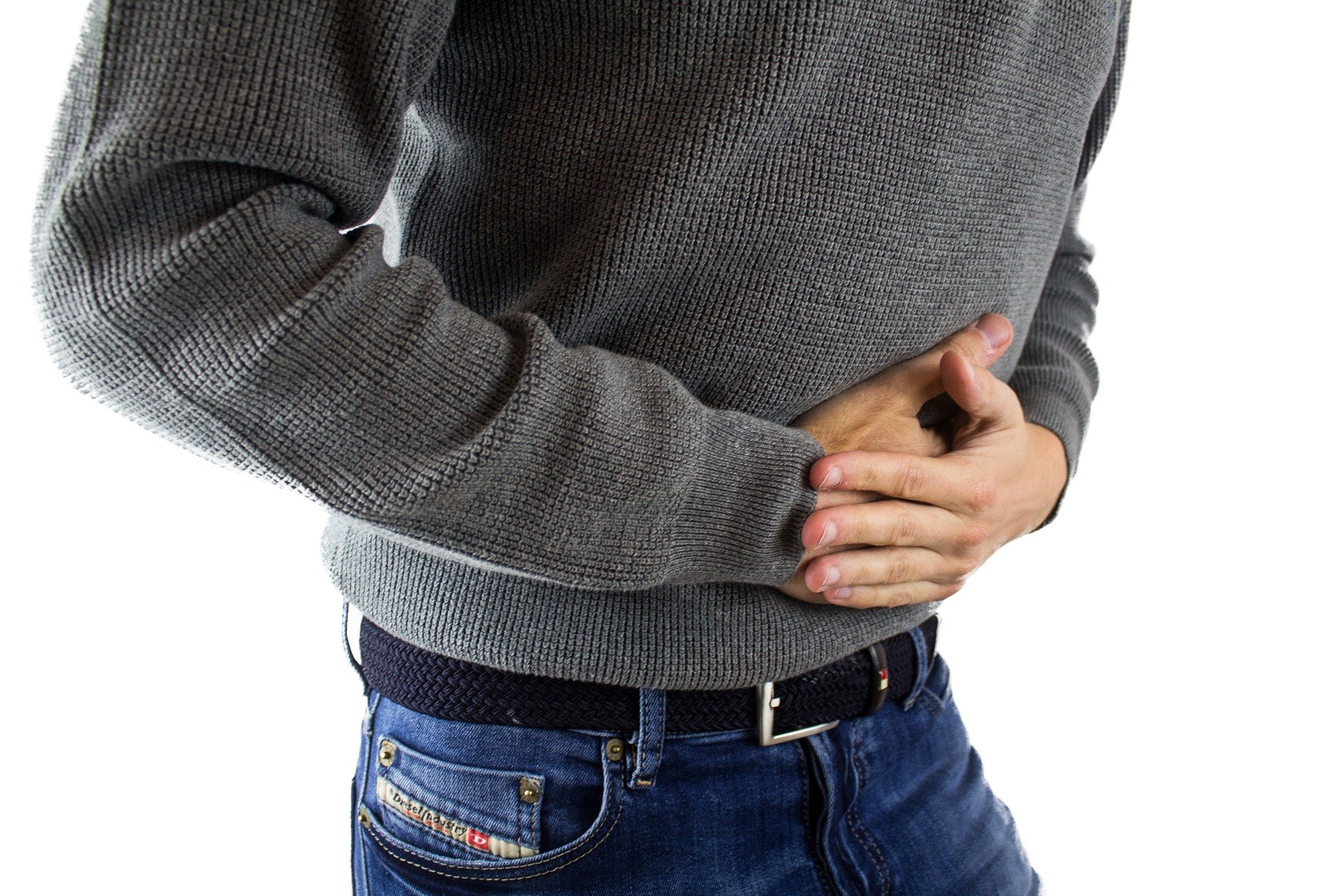
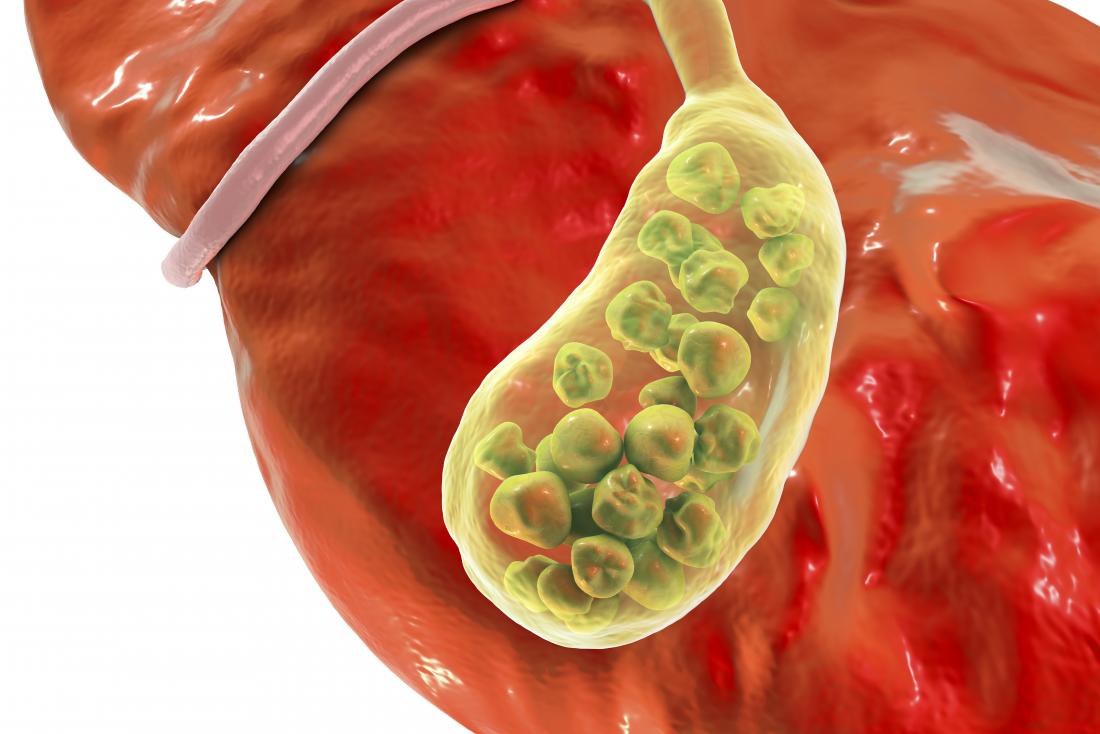
A post-cholecystectomy syndrome occurs when abdominal symptoms, similar to gallstones, arise after gallbladder surgery. This syndrome is temporary and heals with medications.
CAUSES
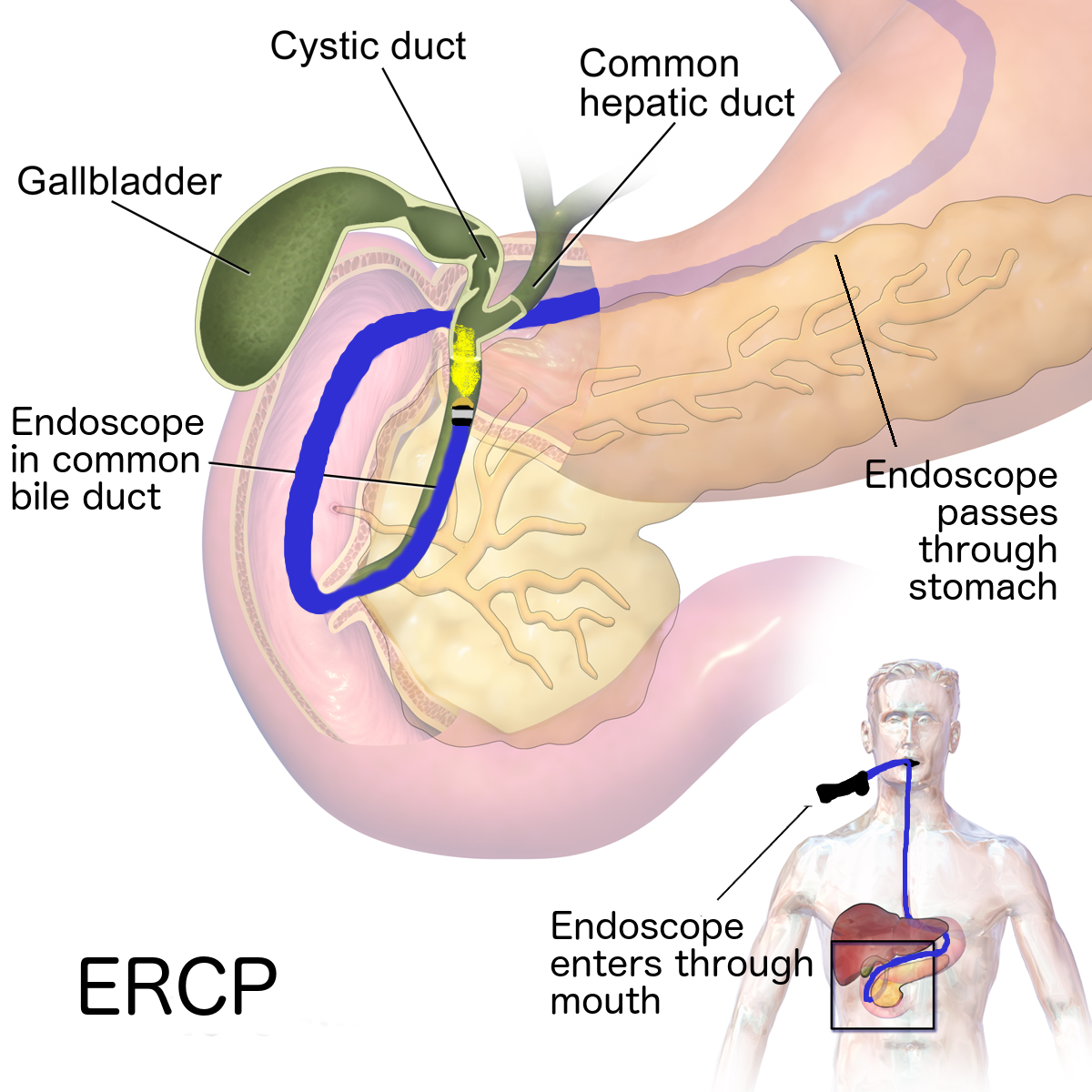
Post-cholecystectomy syndrome (PCS) is thought to be caused by bile leaking into areas such as the stomach, or by gallstones being left in the bile ducts after the gall bladder stone surgery.
RISK FACTORS
About 5% to 40% of people who have the gallbladder removed may experience postcholecystectomy syndrome symptoms. (Source)
SYMPTOMS
The most common symptoms of a postcholecystectomy syndrome include:
- Bloating
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Upset stomach
- Persistent pain in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen
- Gas
TREATMENT
In most cases symptoms of PCS are mild and short-lived, but they can persist for many months.
If you have persistent symptoms, you should contact your doctor for advice.
You may benefit from a procedure to remove any remaining gallstones, or medication to relieve your symptoms.
Laparoscopic Gallstone surgery has very few complications as compared to many other major surgeries. However, it may still result in postcholecystectomy syndrome on rare occasions. In these cases, you must consult your doctor if symptoms don’t go away with time.
REFERENCE
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3473449/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539902/
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gallbladder-removal/risks/
- https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/aa99893#aa99893-sec