Coeliac disease
OVERVIEW | CAUSES | RISK FACTORS | SYMPTOMS | COMPLICATION | DIAGNOSIS | TREATMENT | PREVENTION | REFERENCES

OVERVIEW
Celiac disease, sometimes called celiac sprue or gluten-sensitive enteropathy, is an immune reaction to eating gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye.If you have celiac disease, eating gluten triggers an immune response in your small intestine. Over time, this reaction damages your small intestine's lining and prevents it from absorbing some nutrients (malabsorption). The intestinal damage often causes diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, bloating and anemia, and can lead to serious complications.In children, malabsorption can affect growth and development, besides causing the symptoms seen in adults.There's no cure for celiac disease — but for most people, following a strict gluten-free diet can help manage symptoms and promote intestinal healing.
CAUSES
Your genes combined with eating foods with gluten and other factors can contribute to celiac disease, but the precise cause isn't known. Infant-feeding practices, gastrointestinal infections and gut bacteria might contribute, as well. Sometimes celiac disease becomes active after surgery, pregnancy, childbirth, viral infection or severe emotional stress.
When the body's immune system overreacts to gluten in food, the reaction damages the tiny, hairlike projections (villi) that line the small intestine. Villi absorb vitamins, minerals and other nutrients from the food you eat. If your villi are damaged, you can't get enough nutrients, no matter how much you eat.
RISK FACTORS
Celiac disease tends to be more common in people who have:
- A family member with celiac disease or dermatitis herpetiformis
- Type 1 diabetes
- Down syndrome or Turner syndrome
- Autoimmune thyroid disease
- Microscopic colitis (lymphocytic or collagenous colitis)
-
Addison's disease
SYMPTOMS
The signs and symptoms of celiac disease can vary greatly and differ in children and adults. Digestive signs and symptoms for adults include:
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Bloating and gas
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation
However, more than half the adults with celiac disease have signs and symptoms unrelated to the digestive system, including:
- Anemia, usually from iron deficiency
- Loss of bone density (osteoporosis) or softening of bone (osteomalacia)
- Itchy, blistery skin rash (dermatitis herpetiformis)
- Mouth ulcers
- Headaches and fatigue
- Nervous system injury, including numbness and tingling in the feet and hands, possible problems with balance, and cognitive impairment
- Joint pain
- Reduced functioning of the spleen (hyposplenism)
Children
Children with celiac disease are more likely than adults to have digestive problems, including:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Chronic diarrhea
- Swollen belly
- Constipation
- Gas
- Pale, foul-smelling stools
The inability to absorb nutrients might result in:
- Failure to thrive for infants
- Damage to tooth enamel
- Weight loss
- Anemia
- Irritability
- Short stature
- Delayed puberty
- Neurological symptoms, including attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), learning disabilities, headaches, lack of muscle coordination and seizures
Dermatitis herpetiformis
Gluten intolerance can cause this itchy, blistering skin disease. The rash usually occurs on the elbows, knees, torso, scalp and buttocks. This condition is often associated with changes to the lining of the small intestine identical to those of celiac disease, but the skin condition might not cause digestive symptoms.
Doctors treat dermatitis herpetiformis with a gluten-free diet or medication, or both, to control the rash.
COMPLICATIONS
Untreated, celiac disease can cause:
- Malnutrition. This occurs if your small intestine can't absorb enough nutrients. Malnutrition can lead to anemia and weight loss. In children, malnutrition can cause slow growth and short stature.
- Bone weakening. Malabsorption of calcium and vitamin D can lead to a softening of the bone (osteomalacia or rickets) in children and a loss of bone density (osteopenia or osteoporosis) in adults.
- Infertility and miscarriage. Malabsorption of calcium and vitamin D can contribute to reproductive issues.
- Lactose intolerance. Damage to your small intestine might cause you abdominal pain and diarrhea after eating or drinking dairy products that contain lactose. Once your intestine has healed, you might be able to tolerate dairy products again.
- Cancer. People with celiac disease who don't maintain a gluten-free diet have a greater risk of developing several forms of cancer, including intestinal lymphoma and small bowel cancer.
- Nervous system problems. Some people with celiac disease can develop problems such as seizures or a disease of the nerves to the hands and feet (peripheral neuropathy).
Nonresponsive celiac disease
Some people with celiac disease don't respond to what they consider to be a gluten-free diet. Nonresponsive celiac disease is often due to contamination of the diet with gluten. Working with a dietitian can help you learn how to avoid all gluten.
People with nonresponsive celiac disease might have:
- Bacteria in the small intestine (bacterial overgrowth)
- Microscopic colitis
- Poor pancreas function (pancreatic insufficiency)
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Difficulty digesting sugar found in dairy products (lactose), table sugar (sucrose), or a type of sugar found in honey and fruits (fructose)
- Refractory celiac disease
Refractory celiac disease
In rare instances, the intestinal injury of celiac disease doesn't respond to a strict gluten-free diet. This is known as refractory celiac disease. If you still have signs and symptoms after following a gluten-free diet for six months to one year, you might need further testing to look for other explanations for your symptoms.
DIAGNOSIS
Many people with celiac disease don't know they have it. Two blood tests can help diagnose it:
- Serology testing looks for antibodies in your blood. Elevated levels of certain antibody proteins indicate an immune reaction to gluten.
- Genetic testing for human leukocyte antigens (HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8) can be used to rule out celiac disease.
It's important to be tested for celiac disease before trying a gluten-free diet. Eliminating gluten from your diet might make the results of blood tests appear normal.
If the results of these tests indicate celiac disease, your doctor will likely order one of the following tests:
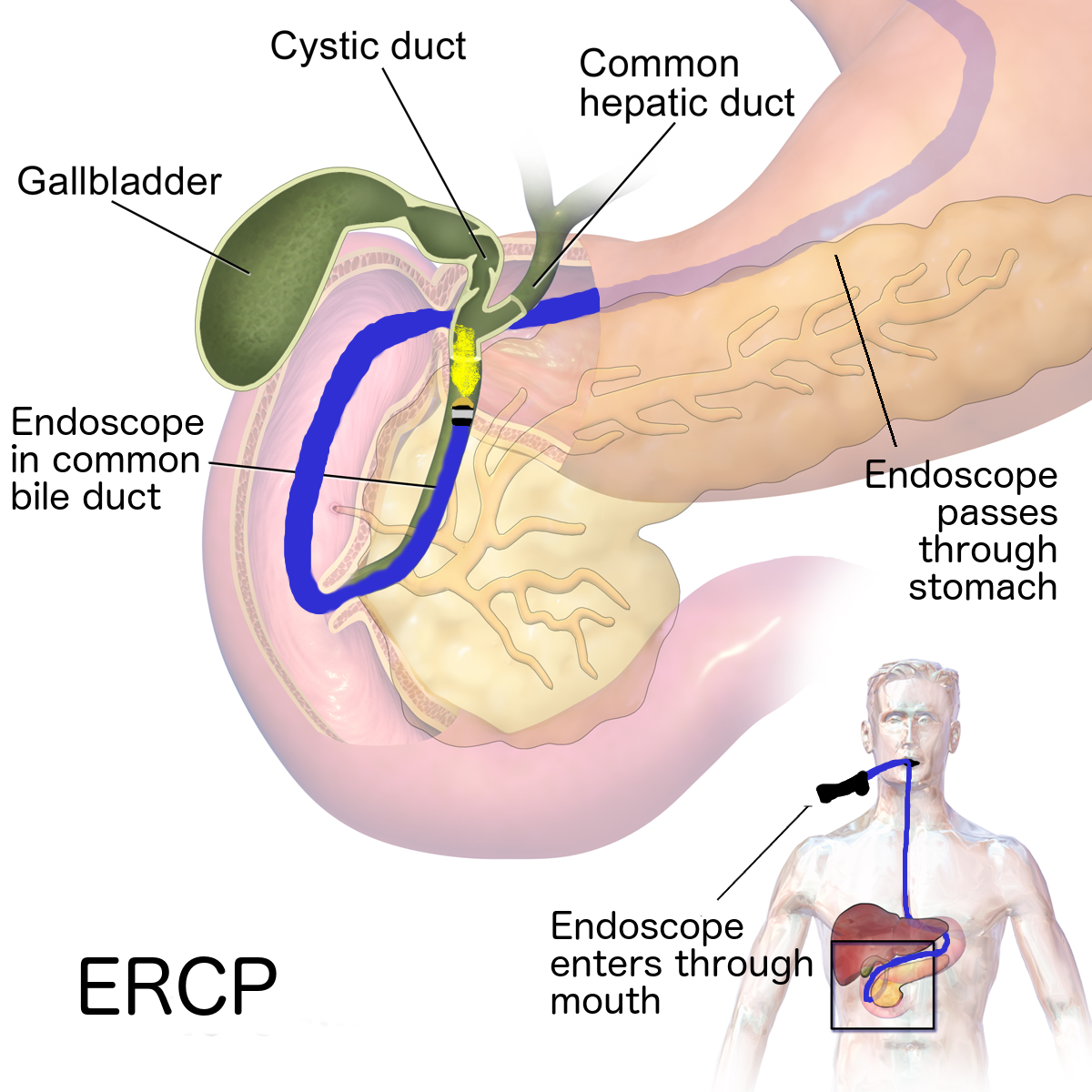
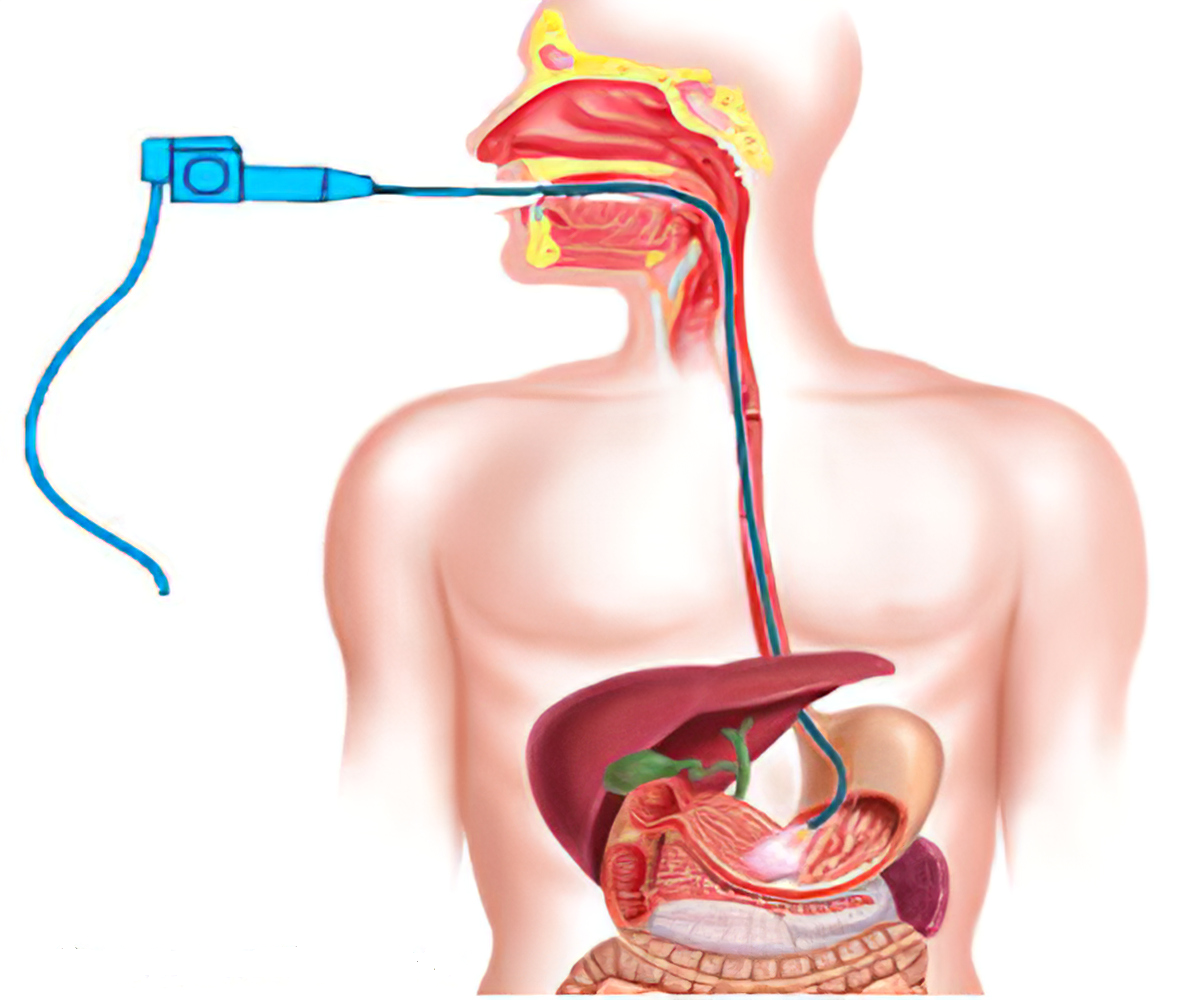
- Endoscopy. This test uses a long tube with a tiny camera that's put into your mouth and passed down your throat (upper endoscopy). The camera enables your doctor to view your small intestine and take a small tissue sample (biopsy) to analyze for damage to the villi.
- Capsule endoscopy. This test uses a tiny wireless camera to take pictures of your entire small intestine. The camera sits inside a vitamin-sized capsule, which you swallow. As the capsule travels through your digestive tract, the camera takes thousands of pictures that are transmitted to a recorder.
If your doctor suspects you have dermatitis herpetiformis, he or she might take a small sample of skin tissue to examine under a microscope (skin biopsy).
TREATMENT
A strict, lifelong gluten-free diet is the only way to manage celiac disease. Besides wheat, foods that contain gluten include:
- Barley
- Bulgur
- Durum
- Farina
- Graham flour
- Malt
- Rye
- Semolina
- Spelt (a form of wheat)
- Triticale
A dietitian who works with people with celiac disease can help you plan a healthy gluten-free diet. Even trace amounts of gluten in your diet can be damaging, even if they don't cause signs or symptoms.
Gluten can be hidden in foods, medications and nonfood products, including:
- Modified food starch, preservatives and food stabilizers
- Prescription and over-the-counter medications
- Vitamin and mineral supplements
- Herbal and nutritional supplements
- Lipstick products
- Toothpaste and mouthwash
- Communion wafers
- Envelope and stamp glue
- Play dough
Removing gluten from your diet will gradually reduce inflammation in your small intestine, causing you to feel better and eventually heal. Children tend to heal more quickly than adults.
Vitamin and mineral supplements
If your anemia or nutritional deficiencies are severe, your doctor or dietitian might recommend that you take supplements, including:
- Copper
- Folate
- Iron
- Vitamin B-12
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin K
- Zinc
Vitamins and supplements are usually taken in pill form. If your digestive tract has trouble absorbing vitamins, your doctor might give them by injection.
Follow-up care
Medical follow-up at regular intervals can ensure that your symptoms have responded to a gluten-free diet. Your doctor will monitor your response with blood tests.
For most people with celiac disease, a gluten-free diet will allow the small intestine to heal. For children, that usually takes three to six months. For adults, complete healing might take several years.
If you continue to have symptoms or if symptoms recur, you might need an endoscopy with biopsies to determine whether your intestine has healed.
PREVENTION
Celiac disease can't be prevented.
If you already have celiac disease, you can prevent symptoms- and damage to your small intestine- by eating a gluten-free diet.
Some adults with celiac disease have a poorly functioning or nonfunctional spleen, which is a risk factor for developing a pneumococcal infection. For this reason, your doctor may recommend that you get immunized with the pneumococcal vaccine.
REFERENCE
- https://patient.info/digestive-health/coeliac-disease-leaflet
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/celiac-disease/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5437500/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6284033/