Motion Sickness
Overview | Possible Causes | Care and Treatment | HOME REMEDies | When to Call the Doctor | References

Overview
Motion sickness is a common problem in people traveling by car, train, airplanes, and especially boats. Anyone can get it, but it is more common in children, pregnant women, and people taking certain medicines. Motion sickness can start suddenly, with a queasy feeling and cold sweats. It can then lead to dizziness and nausea and vomiting.
These factors increase your chances of getting motion sickness:
- Family history of motion sickness.
- Hormonal birth control.
- Inner ear disorders.
- Menstrual periods.
- Migraines.
- Parkinson’s disease.
- Pregnancy.
Possible Causes
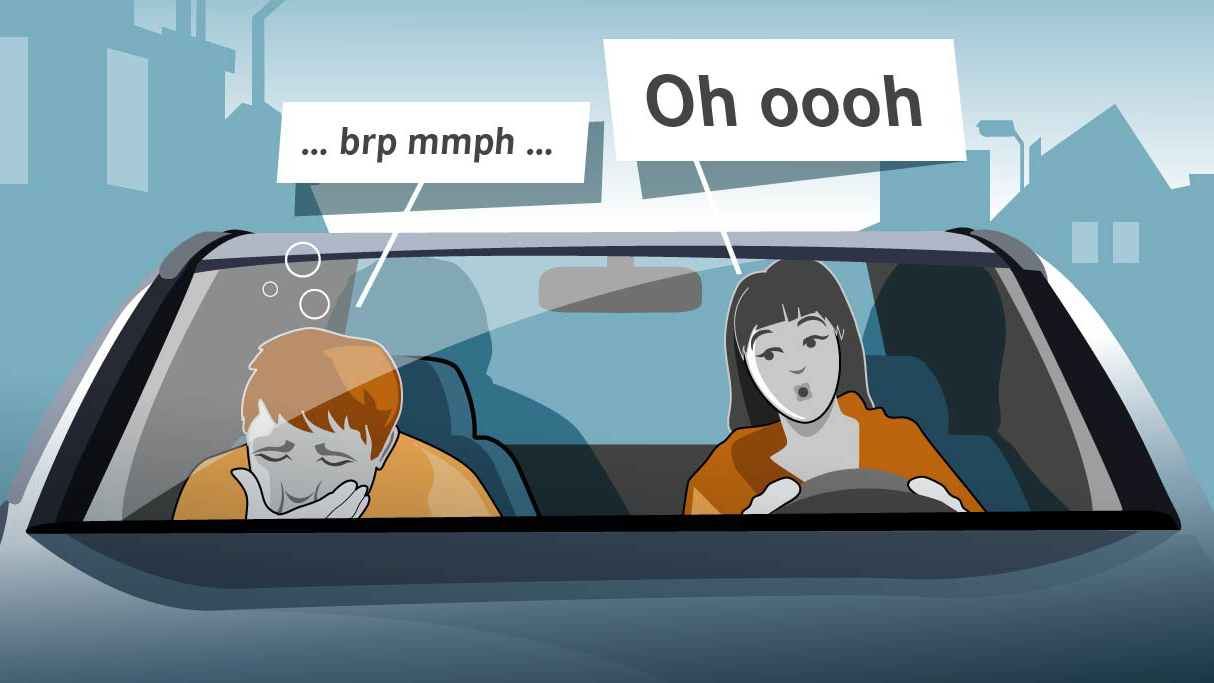
Your brain receives signals from motion-sensing parts of your body: your eyes, inner ears, muscles and joints. When these parts send conflicting information, your brain doesn’t know whether you’re stationary or moving. Your brain’s confused reaction makes you feel sick.
For example, when riding in a car, your:
- Eyes see trees passing by and register movement.
- Inner ears sense movement.
- Muscles and joints sense that your body is sitting still.
- Brain senses a disconnect among these messages.
Many actions can trigger motion sickness, such as:
- Amusement park rides and virtual reality experiences.
- Reading while in motion.
- Riding in a boat, car, bus, train or plane.
- Video games and movies.
Care & Treatment
You have some options to prevent motion sickness or treat symptoms. Motion sickness treatments include:
- Antihistamines: Commonly used to treat allergies, antihistamines can also prevent motion sickness and ease symptoms. Only antihistamines that cause drowsiness are effective. Non-drowsy formulas won’t help.
- Patches: Scopolamine skin patches or oral pills prevent nausea and vomiting. You stick the patch behind your ear at least four hours before travelling. After three days, you remove the patch and apply a new one. This medication can cause dry mouth and is only approved for adults.
Home Remedies
These actions can lower your chances of getting sick or ease symptoms if they occur:
- Herbs: Breathe in soothing mint, ginger or lavender scents. Suck on hard candies made with peppermint or ginger.
- Diet and drink: Drink plenty of water. Choose low-fat, bland, starchy foods before travelling. Avoid heavy meals and greasy, spicy or acidic foods that can upset your stomach. Don’t drink alcohol or smoke.
- Fresh air: Direct air vents to blow toward you. And roll down windows in cars.
- Distant gaze: Put down the phone, tablet or book. Instead, look at an object in the distance or at the horizon.
- Lie back: Recline, if possible, and close your eyes.
- Pressure points: Wear acupressure wristbands.
You should always face forward when travelling. Where you sit can also make a difference to minimize disruptive motion:
- Boat: Sit in the middle of the boat on the upper deck.
- Bus: Choose a window seat.
- Car: Sit in the front passenger seat.
- Cruise ship: Book a cabin toward the front or middle of the ship. If you can, choose one on a lower level, closer to the water.
- Plane: Sit in the wing section.
- Train: Choose a forward-facing window seat.
When to Call the Doctor
You should call your healthcare provider if you experience:
- Chronic, persistent nausea or vomiting.
- Motion sickness symptoms when you’re not involved in a moving activity.
- Signs of dehydration.
Reference
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/12782-motion-sickness
- https://medlineplus.gov/motionsickness.html
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-motion-sickness/basics/art-20056697