Irritable Bowel Syndrome
OVERVIEW | CAUSES | RISK FACTORS | SYMPTOMS | COMPLICATION | Diagnosis | TREATMENT | PREVENTION | REFERENCES
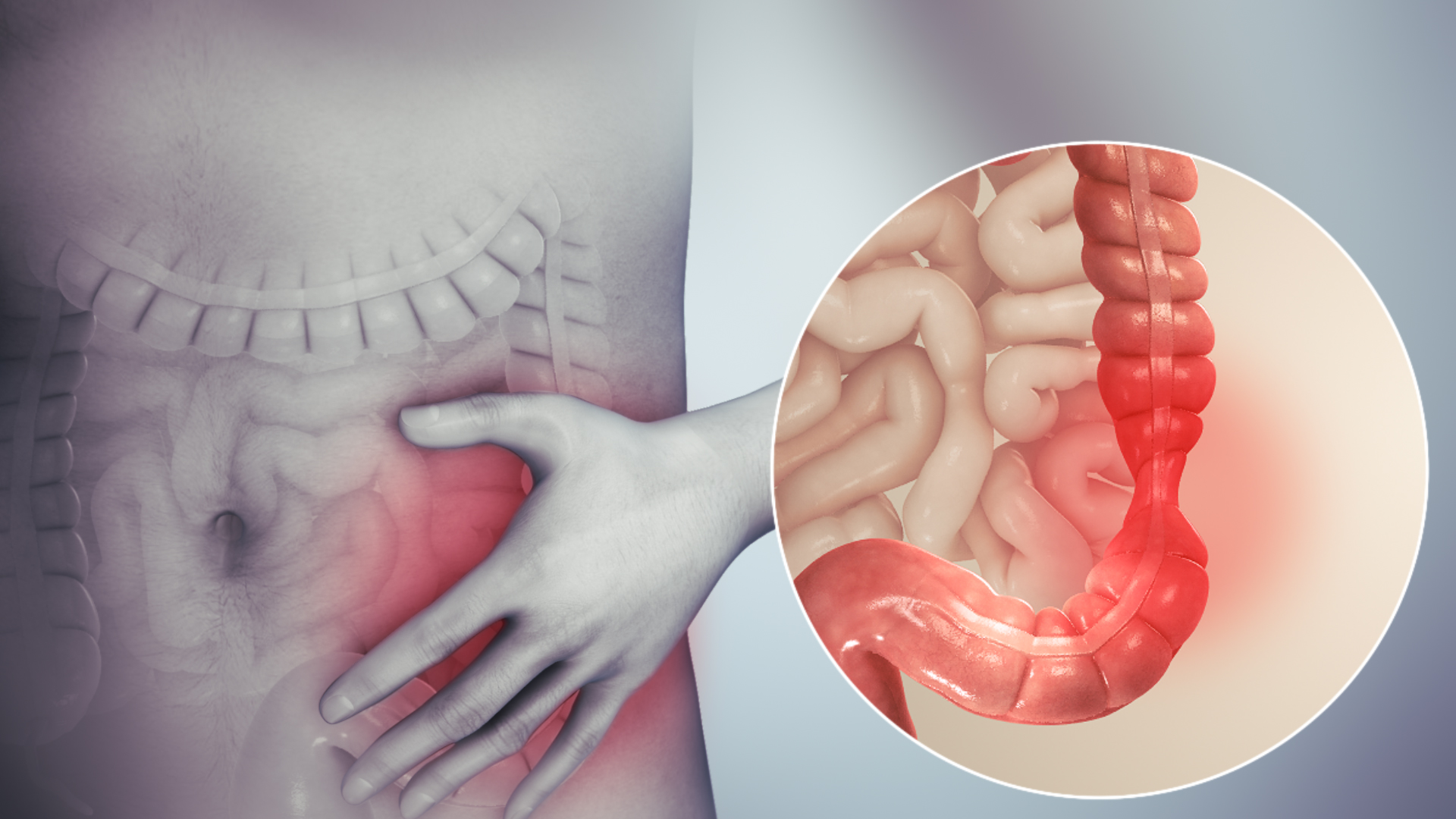
Overview
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common disorder that affects the large intestine. Signs and symptoms include cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and diarrhea or constipation, or both. IBS is a chronic condition that you'll need to manage long term.
Only a small number of people with IBS have severe signs and symptoms. Some people can control their symptoms by managing diet, lifestyle and stress. More-severe symptoms can be treated with medication and counseling.
IBS doesn't cause changes in bowel tissue or increase your risk of colorectal cancer.
Causes
The precise cause of IBS isn't known. Factors that appear to play a role include:
- Muscle contractions in the intestine. The walls of the intestines are lined with layers of muscle that contract as they move food through your digestive tract. Contractions that are stronger and last longer than normal can cause gas, bloating and diarrhea. Weak intestinal contractions can slow food passage and lead to hard, dry stools.
- Nervous system. Abnormalities in the nerves in your digestive system may cause you to experience greater than normal discomfort when your abdomen stretches from gas or stool. Poorly coordinated signals between the brain and the intestines can cause your body to overreact to changes that normally occur in the digestive process, resulting in pain, diarrhea or constipation.
- Severe infection. IBS can develop after a severe bout of diarrhea (gastroenteritis) caused by bacteria or a virus. IBS might also be associated with a surplus of bacteria in the intestines (bacterial overgrowth).
- Early life stress. People exposed to stressful events, especially in childhood, tend to have more symptoms of IBS.
- Changes in gut microbes. Examples include changes in bacteria, fungi and viruses, which normally reside in the intestines and play a key role in health. Research indicates that the microbes in people with IBS might differ from those in healthy people.
Triggers
Symptoms of IBS can be triggered by:
- Food. The role of food allergy or intolerance in IBS isn't fully understood. A true food allergy rarely causes IBS. But many people have worse IBS symptoms when they eat or drink certain foods or beverages, including wheat, dairy products, citrus fruits, beans, cabbage, milk and carbonated drinks.
- Stress. Most people with IBS experience worse or more-frequent signs and symptoms during periods of increased stress. But while stress may aggravate symptoms, it doesn't cause them.
Risk factors
Many people have occasional signs and symptoms of IBS. But you're more likely to have the syndrome if you:
- Are young. IBS occurs more frequently in people under age 50.
- Are female. In the United States, IBS is more common among women. Estrogen therapy before or after menopause also is a risk factor for IBS.
- Have a family history of IBS. Genes may play a role, as may shared factors in a family's environment or a combination of genes and environment.
- Have anxiety, depression or other mental health issues. A history of sexual, physical or emotional abuse also might be a risk factor.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of IBS vary but are usually present for a long time. The most common include:
- Abdominal pain, cramping or bloating that is related to passing a bowel movement
- Changes in appearance of bowel movement
- Changes in how often you are having a bowel movement
Other symptoms that are often related include bloating, increased gas or mucus in the stool.
Complications
Chronic constipation or diarrhea can cause hemorrhoids.
In addition, IBS is associated with:
- Poor quality of life. Many people with moderate to severe IBS report poor quality of life. Research indicates that people with IBS miss three times as many days from work as do those without bowel symptoms.
- Mood disorders. Experiencing the signs and symptoms of IBS can lead to depression or anxiety. Depression and anxiety also can make IBS worse
Diagnosis
There's no test to definitively diagnose IBS. Your doctor is likely to start with a complete medical history, physical exam and tests to rule out other conditions, such as celiac disease.
After other conditions have been ruled out, your doctor is likely to use one of these sets of diagnostic criteria for IBS:
- Rome criteria. These criteria include abdominal pain and discomfort lasting on average at least one day a week in the last three months, associated with at least two of these factors: Pain and discomfort are related to defecation, the frequency of defecation is altered, or stool consistency is altered.
- Type of IBS. For the purpose of treatment, IBS can be divided into three types, based on your symptoms: constipation-predominant, diarrhea-predominant or mixed.
Your doctor will also likely assess whether you have other signs or symptoms that might suggest another, more serious, condition. These signs and symptoms include:
- Onset of signs and symptoms after age 50
- Weight loss
- Rectal bleeding
- Fever
- Nausea or recurrent vomiting
- Abdominal pain, especially if it's not related to a bowel movement, or occurs at night
- Diarrhea that is persistent or awakens you from sleep
- Anemia related to low iron
If you have these signs or symptoms, or if an initial treatment for IBS doesn't work, you'll likely need additional tests.
Additional tests
Your doctor may recommend several tests, including stool studies to check for infection or problems with your intestine's ability to take in the nutrients from food (malabsorption). You may also have a number of other tests to rule out other causes for your symptoms.
Diagnostic procedures can include:
- Colonoscopy. Your doctor uses a small, flexible tube to examine the entire length of the colon.
- X-ray or CT scan. These tests produce images of your abdomen and pelvis that might allow your doctor to rule out other causes of your symptoms, especially if you have abdominal pain. Your doctor might fill your large intestine with a liquid (barium) to make any problems more visible on X-ray. This barium test is sometimes called a lower GI series.
- Upper endoscopy. A long, flexible tube is inserted down your throat and into the tube connecting your mouth and stomach (esophagus). A camera on the end of the tube allows the doctor to inspect your upper digestive tract and obtain a tissue sample (biopsy) from your small intestine and fluid to look for overgrowth of bacteria. Your doctor might recommend endoscopy if celiac disease is suspected.
Laboratory tests can include:
- Lactose intolerance tests. Lactase is an enzyme you need to digest the sugar found in dairy products. If you don't produce lactose, you may have problems similar to those caused by IBS, including abdominal pain, gas and diarrhea. Your doctor may order a breath test or ask you to remove milk and milk products from your diet for several weeks.
- Breath test for bacterial overgrowth. A breath test also can determine if you have bacterial overgrowth in your small intestine. Bacterial overgrowth is more common among people who have had bowel surgery or who have diabetes or some other disease that slows down digestion.
- Stool tests. Your stool might be examined for bacteria or parasites, or a digestive liquid produced in your liver (bile acid), if you have chronic diarrhea.
Treatment
Treatment of IBS focuses on relieving symptoms so that you can live as normally as possible.
Mild signs and symptoms can often be controlled by managing stress and by making changes in your diet and lifestyle. Try to:
- Avoid foods that trigger your symptoms
- Eat high-fiber foods
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Exercise regularly
- Get enough sleep
Your doctor might suggest that you eliminate from your diet:
- High-gas foods. If you experience bloating or gas, you might avoid items such as carbonated and alcoholic beverages and certain foods that may lead to increased gas.
- Gluten. Research shows that some people with IBS report improvement in diarrhea symptoms if they stop eating gluten (wheat, barley and rye) even if they don't have celiac disease.
- FODMAPs. Some people are sensitive to certain carbohydrates such as fructose, fructans, lactose and others, known as FODMAPs — fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols. FODMAPs are found in certain grains, vegetables, fruits and dairy products.
A dietitian can help you with these diet changes.
If your problems are moderate or severe, your doctor might suggest counseling — especially if you have depression or if stress tends to worsen your symptoms.
In addition, based on your symptoms your doctor might suggest medications such as:
- Fiber supplements. Taking a supplement such as psyllium (Metamucil) with fluids may help control constipation.
- Laxatives. If fiber doesn't help constipation, your doctor may recommend over-the-counter laxatives, such as magnesium hydroxide oral (Phillips' Milk of Magnesia) or polyethylene glycol (Miralax).
- Anti-diarrheal medications. Over-the-counter medications, such as loperamide (Imodium A-D), can help control diarrhea. Your doctor might also prescribe a bile acid binder, such as cholestyramine (Prevalite), colestipol (Colestid) or colesevelam (Welchol). Bile acid binders can cause bloating.
- Anticholinergic medications. Medications such as dicyclomine (Bentyl) can help relieve painful bowel spasms. They are sometimes prescribed for people who have bouts of diarrhea. These medications are generally safe but can cause constipation, dry mouth and blurred vision.
- Tricyclic antidepressants. This type of medication can help relieve depression as well as inhibit the activity of neurons that control the intestines to help reduce pain. If you have diarrhea and abdominal pain without depression, your doctor may suggest a lower than normal dose of imipramine (Tofranil), desipramine (Norpramin) or nortriptyline (Pamelor). Side effects — which might be reduced if you take the medication at bedtime — can include drowsiness, blurred vision, dizziness and dry mouth.
- SSRI antidepressants. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants, such as fluoxetine (Prozac, Sarafem) or paroxetine (Paxil), may help if you are depressed and have pain and constipation.
- Pain medications. Pregabalin (Lyrica) or gabapentin (Neurontin) might ease severe pain or bloating.
Medications specifically for IBS
Medications approved for certain people with IBS include:
- Alosetron (Lotronex). Alosetron is designed to relax the colon and slow the movement of waste through the lower bowel. Alosetron can be prescribed only by doctors enrolled in a special program, is intended for severe cases of diarrhea-predominant IBS in women who haven't responded to other treatments, and isn't approved for use by men. It has been linked to rare but important side effects, so it should only be considered when other treatments aren't successful.
- Eluxadoline (Viberzi). Eluxadoline can ease diarrhea by reducing muscle contractions and fluid secretion in the intestine, and increasing muscle tone in the rectum. Side effects can include nausea, abdominal pain and mild constipation. Eluxadoline has also been associated with pancreatitis, which can be serious and more common in certain individuals.
- Rifaximin (Xifaxan). This antibiotic can decrease bacterial overgrowth and diarrhea.
- Lubiprostone (Amitiza). Lubiprostone can increase fluid secretion in your small intestine to help with the passage of stool. It's approved for women who have IBS with constipation, and is generally prescribed only for women with severe symptoms that haven't responded to other treatments.
- Linaclotide (Linzess). Linaclotide also can increase fluid secretion in your small intestine to help you pass stool. Linaclotide can cause diarrhea, but taking the medication 30 to 60 minutes before eating might help.
Potential future treatments
Researchers are investigating new treatments for IBS, such as fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT). Considered investigational at this time, FMT restores healthy intestinal bacteria by placing another person's processed stool into the colon of a person affected by IBS. Clinical trials to study fecal transplants are currently underway.
Prevention
You can't prevent irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). But proper self-care may help ease symptoms and may extend the time between episodes. Self-care includes quitting smoking, avoiding caffeine and foods that make symptoms worse, and getting regular exercise.