Surgery
6 Surgeries to Control Obesity
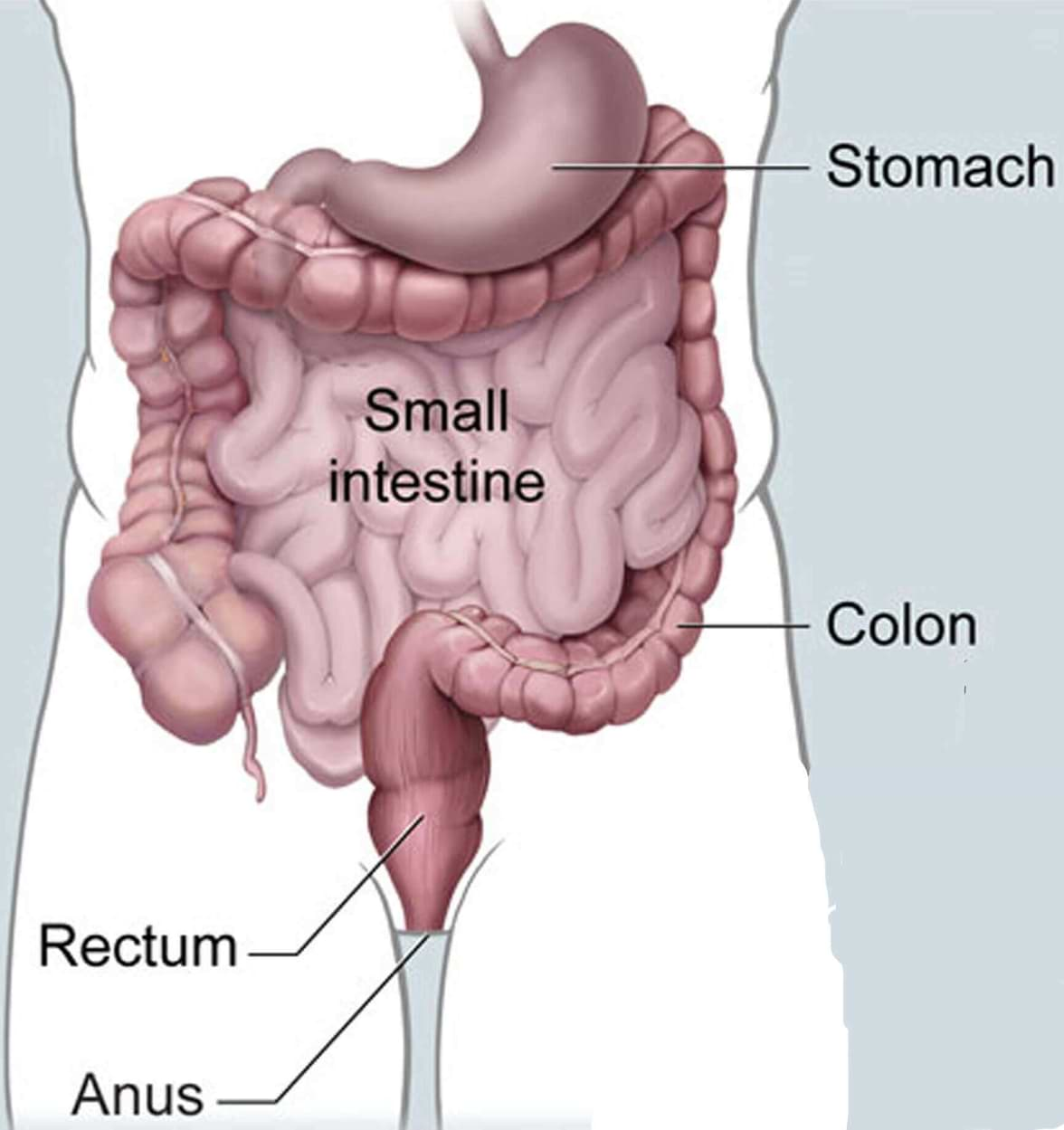
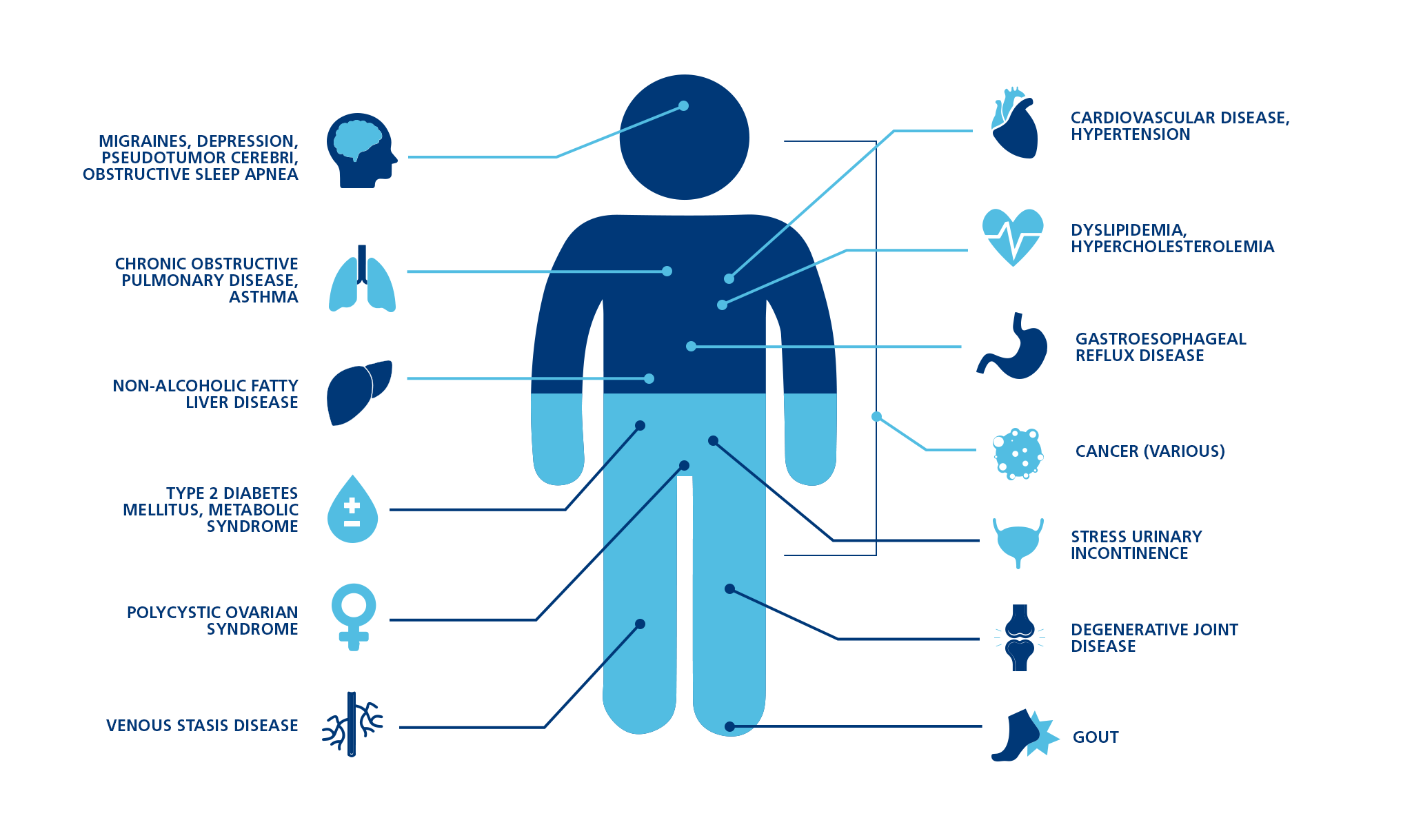
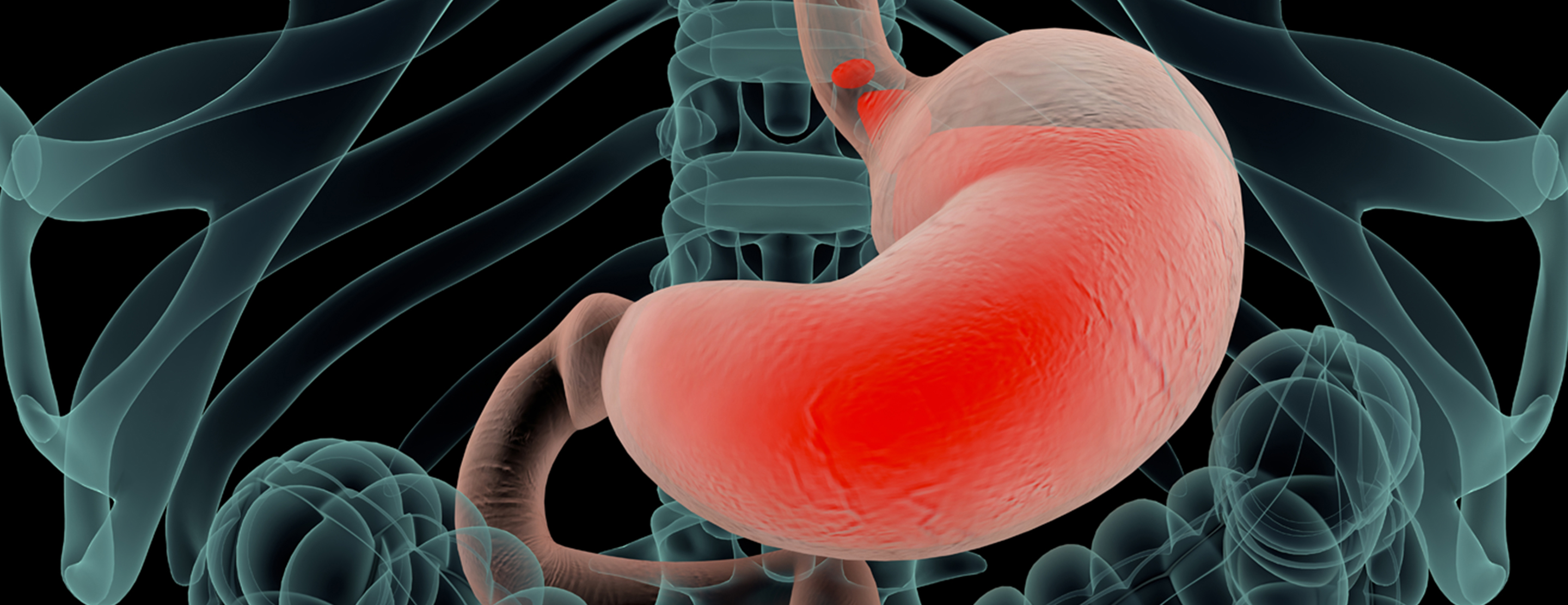
Obesity is a complex disease involving an excessive amount of body fat. Obesity isn't just a cosmetic concern. It is a medical problem that increases your risk of other diseases and health problems, such as heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure and certain cancers.
Summary: 60 Second Read
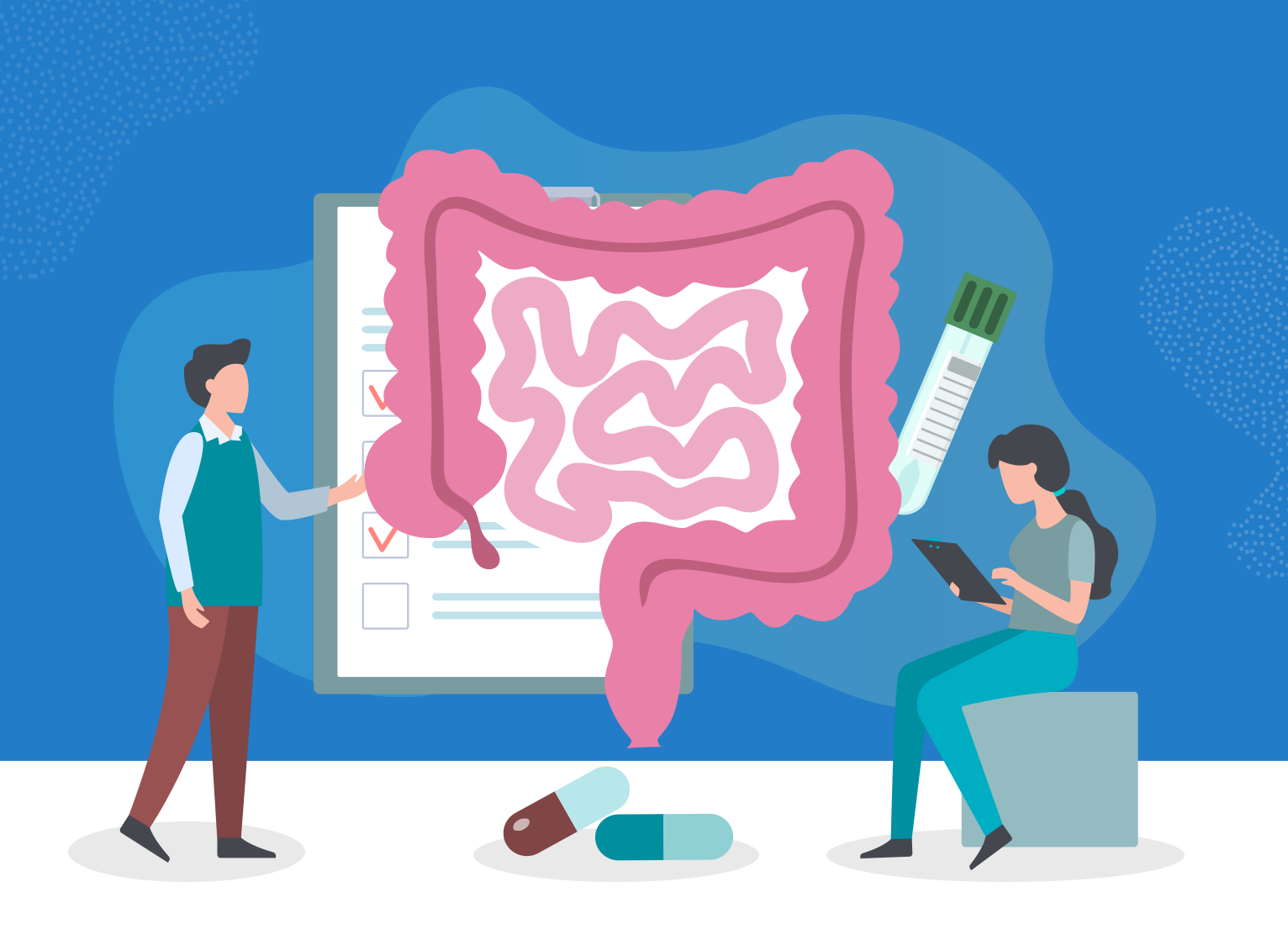
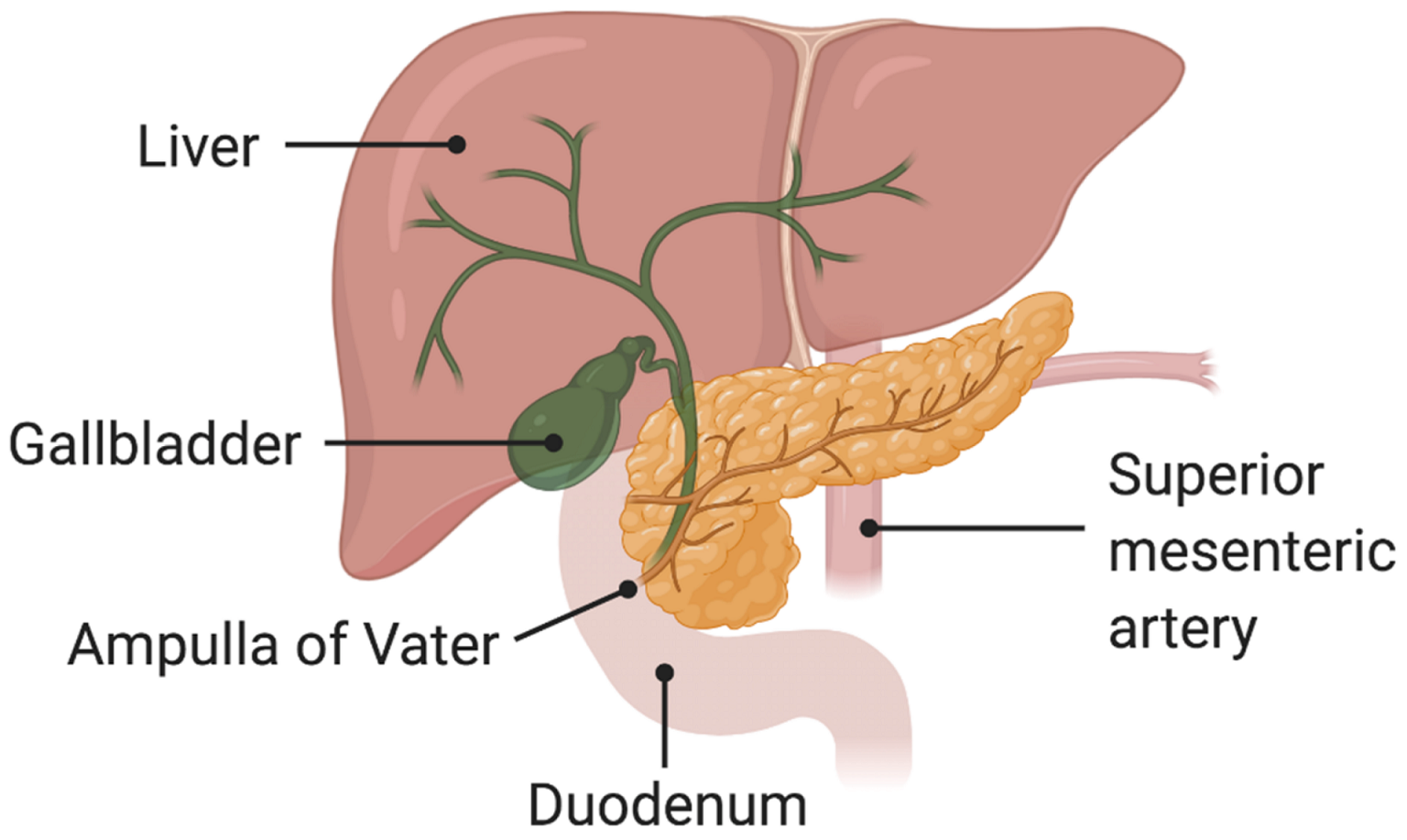
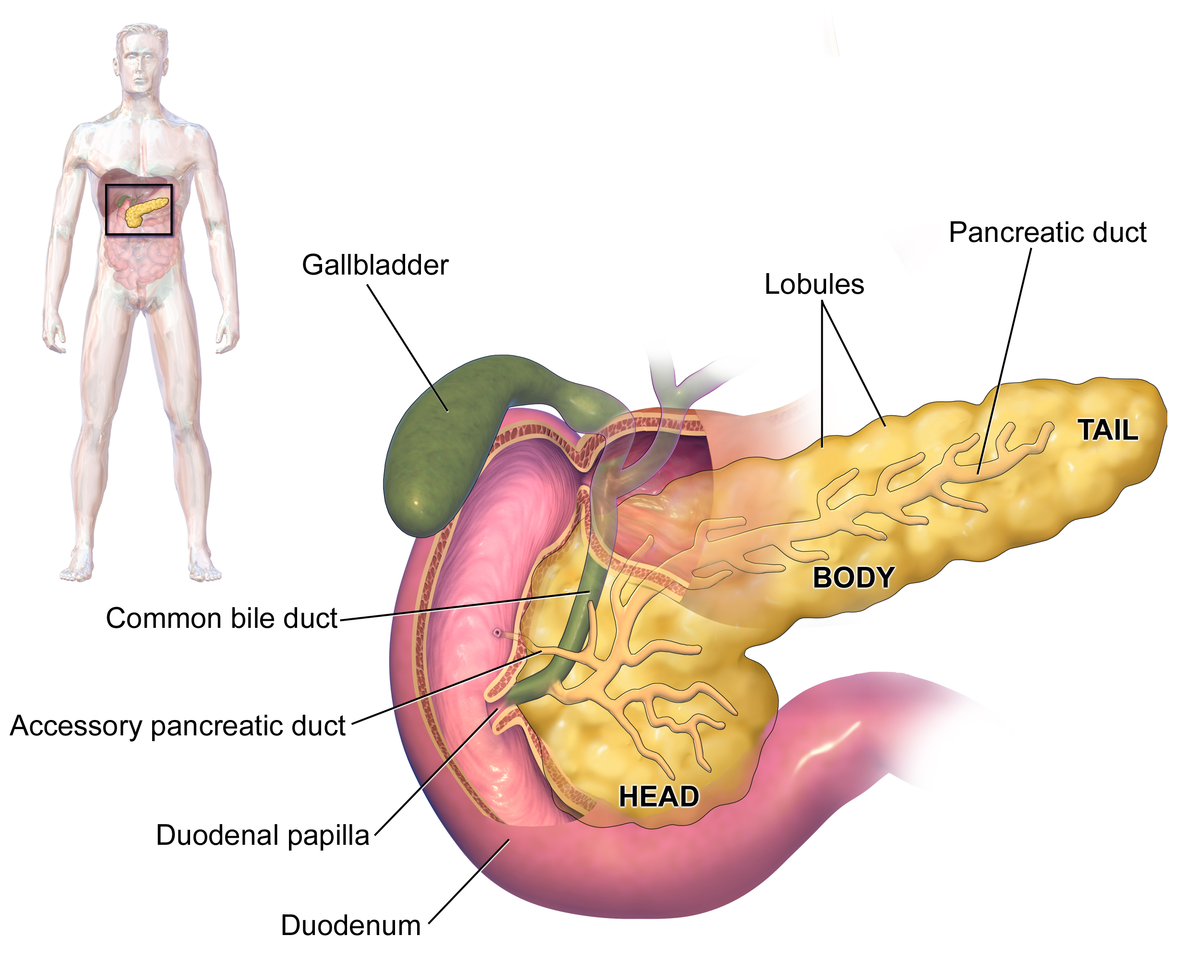
- ADJUSTABLE GASTRIC BAND SURGERY Its purely restrictive and reversible procedure where an inflatable band is applied over the upper part of stomach to create a small pouch of stomach. Among the other procedures, this procedure gives least weight loss.
- SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY This is a restrictive weight loss surgery, where the majority of the stomach is removed. This is generally used for patients with high morbidity and where other means of weight loss are not possible.
- GASTRIC BYPASS SURGERY (ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS) A restrictive and malabsorptive weight loss surgery, where stomach is divided in half top and bottom part and the top part is then connected with lower intestine thereby bypassing major part of stomach and small intestine which results in less calories absorption. This is generally used for patients with high morbidity and where other means of weight loss are not possible.
- MINI GASTRIC BYPASS The Mini-Gastric Bypass or single anastomosis gastric bypass, is an effective and well-established procedure which combines some of the properties of a gastric sleeve and a standard gastric bypass. The upper part of the stomach is divided into a tube, similar to the top three quarters of a sleeve, and then joined to a loop of intestine.
- BILIOPANCREATIC DIVERSION This is a more drastic version of a gastric bypass. The surgeon removes as much as 70% of your stomach and bypasses even more of the small intestine.
- GASTRIC BALLOON/INTRAGASTRIC BALLOON SYSTEM This is a more commonly used and a minimal procedure surgery. This is a reversible surgery and is used with patients which are having trouble with diet restrictions and physical exercise due to some medical conditions or limitations.
Obesity is one of the biggest health problems in the world. It’s associated with several related conditions, collectively known as metabolic syndrome. These include high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar and a poor blood lipid profile.
People with metabolic syndrome are at a much higher risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes, compared to those whose weight is in a normal range.
Over the past decades, much research has focused on the causes of obesity and how it could be prevented or treated.
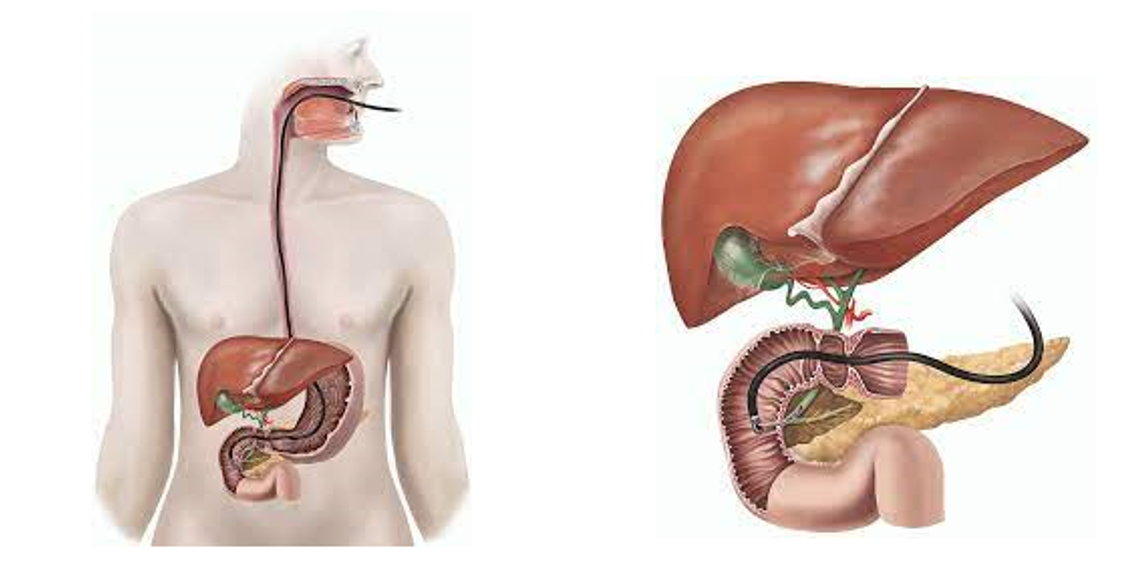
Surgery is one of the ways to treat obesity. Its is generaly chosen when obesity becomes a risk to health and cannot be treated by other alternative methods like Diet Plan, Physical Excersices etc.
Weight loss, or bariatric, surgery involves removing or changing a part of a person’s stomach or small intestine so that they do not consume as much food or absorb as many calories as before.
This can help an individual to lose weight and also reduce the risk of high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and other aspects of metabolic syndrome that can occur with obesity.
Surgery can either make the stomach smaller, or it can bypass part of the digestive system.
Lets check out the top most common bariatric / weight loss surgeries.
1. Adjustable gastric band Surgery
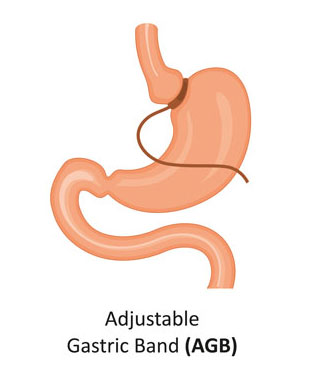
How it works: The surgeon uses an inflatable band to squeeze the stomach into two sections: a smaller upper pouch and a larger lower section. The two sections are still connected by a very small channel, which slows down the emptying of the upper pouch. Most people can only eat a 1/2 to 1 cup of food before feeling too full or sick. The food also needs to be soft or well-chewed.
Pros: This operation is simpler to do and safer than gastric bypass and other operations. You get a smaller scar, recovery is usually faster, and you can have surgery to remove the band.
You can also get the band adjusted in a doctor's office. To tighten the band and further restrict your stomach size, the doctor injects more saline solution into the band. To loosen it, the doctor uses a needle to remove liquid from the band.
Cons: People who get gastric banding often have less dramatic weight loss than those who get other surgeries. They may also be more likely to regain some of the weight over the years.
Risks: One of the most common side effects of gastric banding is vomiting after eating too much too quickly. Complications with the band can happen. It might slip out of place, become too loose, or leak. Some people need more surgeries. As with any operation, infection is a risk. Although unlikely, some complications can be life-threatening.
Summary- Its purely restrictive and reversible procedure where an inflatable band is applied over the upper part of stomach to create a small pouch of stomach. Among the other procedures, this procedure gives least weight loss.
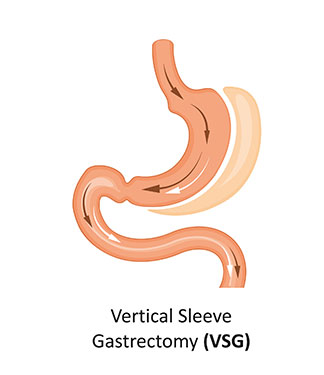
What it is: This is another form of restrictive weight loss surgery. In the operation, the surgeon removes about 75% of the stomach. What remains of the stomach is a narrow tube or sleeve, which connects to the intestines.
Pros: For people who are very obese or sick, other weight loss surgeries may be too risky. A sleeve gastrectomy is a simpler operation that gives them a lower-risk way to lose weight. If needed, once they've lost weight and their health has improved -- usually after 12 to 18 months -- they can have a second surgery, such as gastric bypass.
Because the intestines aren't affected, a sleeve gastrectomy doesn't affect how your body absorbs food, so you're not as likely to fall short on nutrients.
Cons: Unlike gastric banding, a sleeve gastrectomy is irreversible.
Risks: Typical risks include infection, leaking of the sleeve, and blood clots.
Summary- This is a restrictive weight loss surgery, where the majority of the stomach is removed. This is generally used for patients with high morbidity and where other means of weight loss are not possible.
3. Gastric Bypass Surgery (Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass)
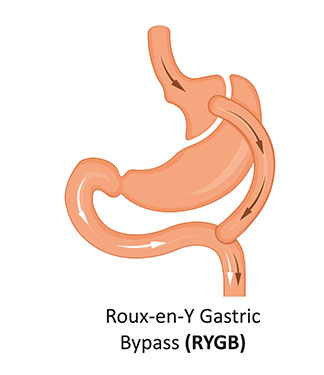
What it is: Gastric bypass combines both restrictive and malabsorptive approaches.
In the operation, the surgeon divides the stomach into two parts, sealing off the upper section from the lower. The surgeon then connects the upper stomach directly to the lower section of the small intestine.
Essentially, the surgeon is creating a shortcut for the food, bypassing part of the stomach and the small intestine. Skipping these parts of the digestive tract means that the body absorbs fewer calories.F
Pros: Weight loss tends to be swift and dramatic. About 50% of it happens in the first 6 months. It may continue for up to 2 years after the operation. Because of the rapid weight loss, conditions affected by obesity -- such as diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, arthritis, sleep apnea, and heartburn -- often get better quickly.(source)
Gastric bypass also has good long-term results. Studies have found that many people keep most of the weight off for 10 years or longer.(source)
Cons: You won't absorb food the way you used to, and that puts you at risk for not getting enough nutrients. The loss of calcium and iron could lead to osteoporosis and anemia. You'll have to be very careful with your diet, and take supplements, for the rest of your life.
Another risk of gastric bypass is dumping syndrome, in which food dumps from the stomach into the intestines too quickly, before it's been properly digested. About 85% of people who get a gastric bypass have some dumping. Symptoms include nausea, bloating, pain, sweating, weakness, and diarrhea. Dumping is often triggered by eating sugary or high-carbohydrate foods, and adjusting your diet can often help.
Unlike adjustable gastric banding, gastric bypass is generally considered irreversible. It has been reversed in rare cases.
Risks: Because gastric bypass is more complicated, it's riskier. Infection and blood clots are risks, as they are with most surgeries. Gastric bypass also makes hernias more likely, which may need further surgery to fix. Also, you may get gallstones because of the rapid weight loss.
Summary- A restrictive and malabsorptive weight loss surgery, where stomach is divided in half top and bottom part and the top part is then connected with lower intestine thereby bypassing major part of stomach and small intestine which results in less calories absorption. This is generally used for patients with high morbidity and where other means of weight loss are not possible.
4. Mini GASTRIC BYPASS SURGERY
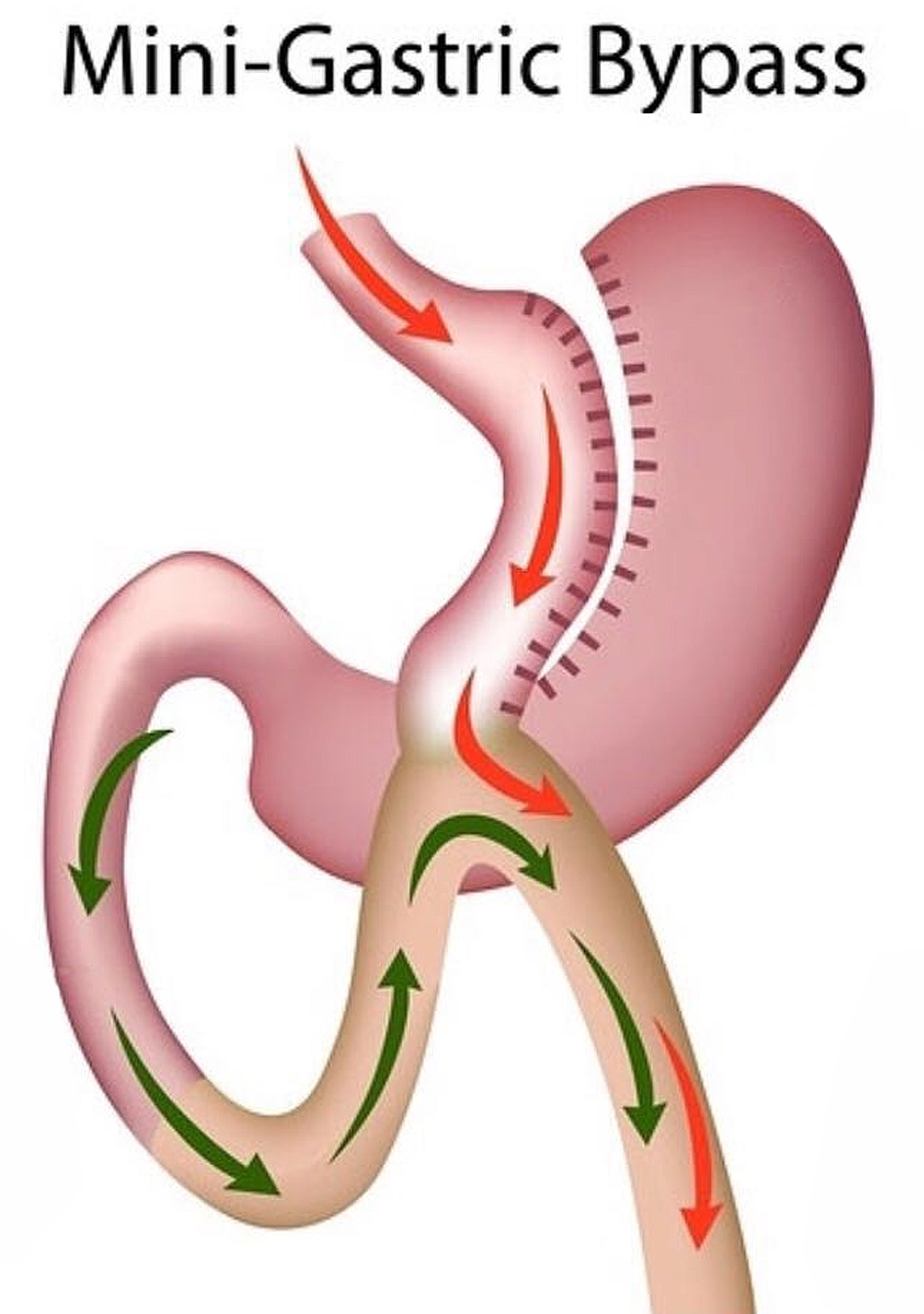
What it is: The Mini-Gastric Bypass or single anastomosis gastric bypass, is an effective and well-established procedure which combines some of the properties of a gastric sleeve and a standard gastric bypass. The upper part of the stomach is divided into a tube, similar to the top three quarters of a sleeve, and then joined to a loop of intestine.
The mini-gastric bypass can be used as a primary weight loss procedure. It can also be used in patients who have had previous gastric banding or sleeve surgery but have been unsuccessful with weight loss, or who have had band-related complications and have decided on revision surgery.
It is not ideally suited to patients with symptoms of reflux disease (severe heartburn that needs medication).
Pros:
- More effective for patients with a higher BMI, compared with standard gastric bypass.
- Most patients have an almost immediate reduction in their need for diabetic medication and some are able to completely stop diabetic medication altogether.
- It does not require any on-going adjustments which are required with other procedures, such as the gastric band.
- It is effective for those people who tend towards high sugar or high fat foods. Dumping syndrome is directly linked to a high sugar, high fat intake. Symptoms of dumping are unpleasant and therefore discourage the intake of high calorie and sweet foods.
Cons:
- Lifelong usage of food supplements and vitamins is necessary for all patients.
- Risk of severe malnutrition requiring reoperation
- Risk of anaemia (low haemoglobin), caused by low iron levels. Women of child-bearing age are most at risk.
- Contrary to common concern, no studies have shown that mini-gastric bypass increases the likelihood of severe reflux or gastroesophageal cancer.
Risks: Possible complications associated with Mini Gastric Bypass can include:
- New intolerances to certain foods
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) with severe heartburn
- Nutritional deficiencies due nutrient malabsorption
- Dumping syndrome
- Staple line leaks
- Vomiting, nausea, diarrhoea
- Strictures
- Bowel obstruction
- Blood clot
Summary- The Mini-Gastric Bypass or single anastomosis gastric bypass, is an effective and well-established procedure which combines some of the properties of a gastric sleeve and a standard gastric bypass. The upper part of the stomach is divided into a tube, similar to the top three quarters of a sleeve, and then joined to a loop of intestine.
Junk foods can cause addiction in susceptible individuals. These people lose control over their eating behavior, similar to people struggling with alcohol addiction losing control over their drinking behavior.
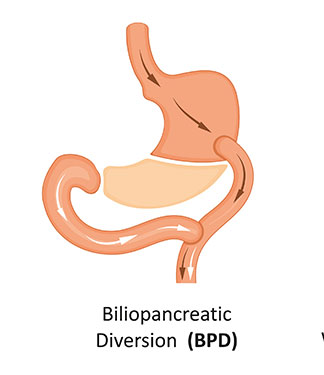
A somewhat less extreme version is biliopancreatic diversion with a duodenal switch, or “the duodenal switch.” It's still more involved than a gastric bypass, but this procedure removes less of the stomach and bypasses less of the small intestinethan biliopancreatic diversion without the switch. It also makes dumping syndrome, malnutrition, and ulcers less common than with a standard biliopancreatic diversion.
Pros: Biliopancreatic diversion can result in even greater and faster weight loss than a gastric bypass. Although much of the stomach is removed, what's left is still larger than the pouches formed during gastric bypass or banding procedures. So you may be able to eat larger meals with this surgery than with others.
Cons: Biliopancreatic diversion is less common than gastric bypass. One of the reasons is that the risk of not getting enough nutrients is much more serious. It also poses many of the same risks as gastric bypass, including dumping syndrome. But the duodenal switch may lower some of these risks.
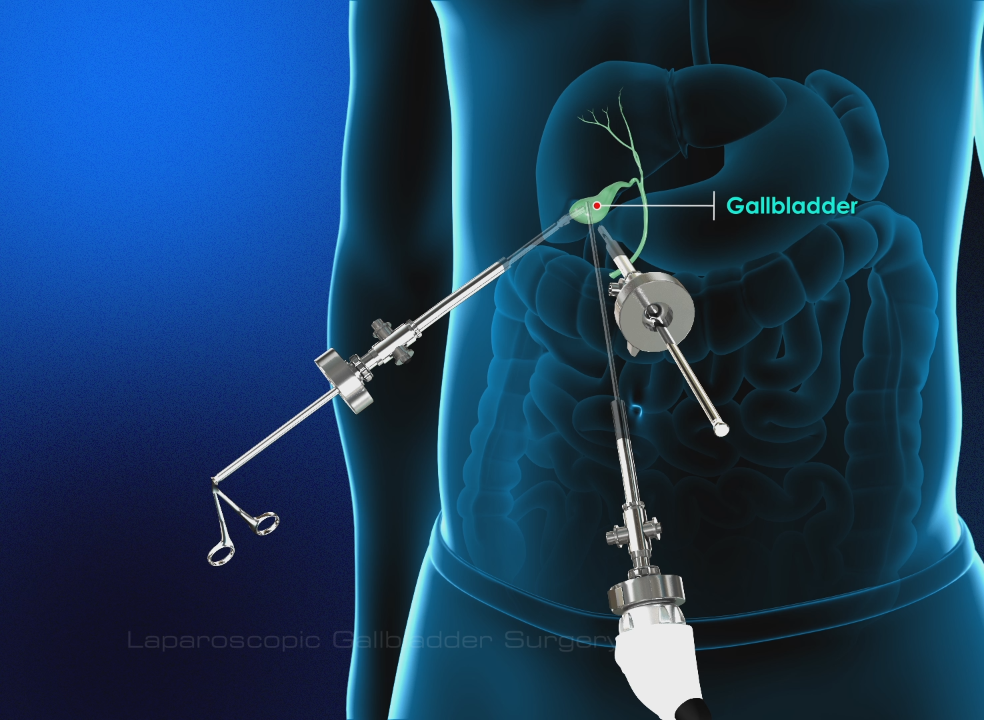
Risks: This is one of the most complicated and riskiest weight loss surgeries. As with gastric bypass, this surgery poses a fairly high risk of hernias, which will need more surgery to correct. But this risk is lower when the doctor uses minimally invasive procedures (called laparoscopy).
Summary- This is a more drastic version of a gastric bypass. The surgeon removes as much as 70% of your stomach and bypasses even more of the small intestine.
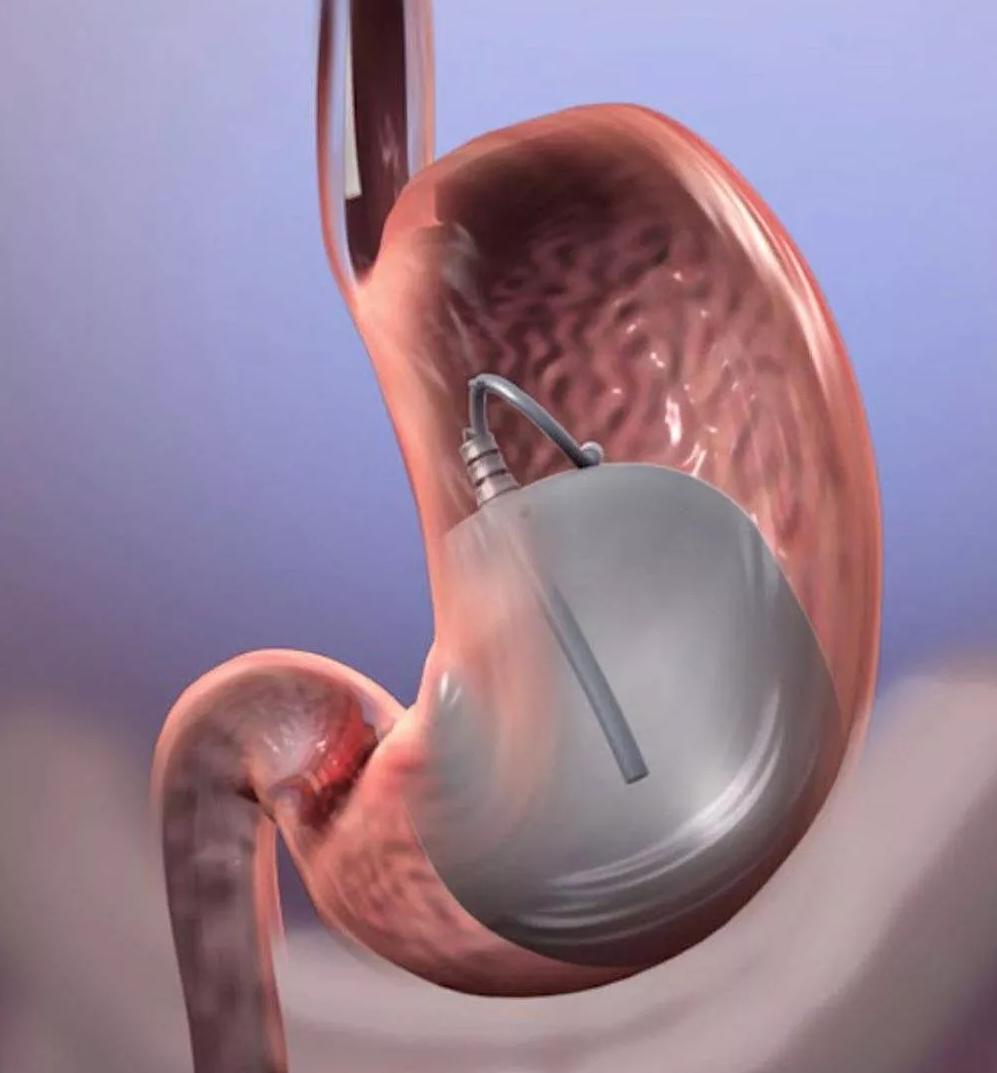
6. Gastric Balloon/Intragastric Balloon System
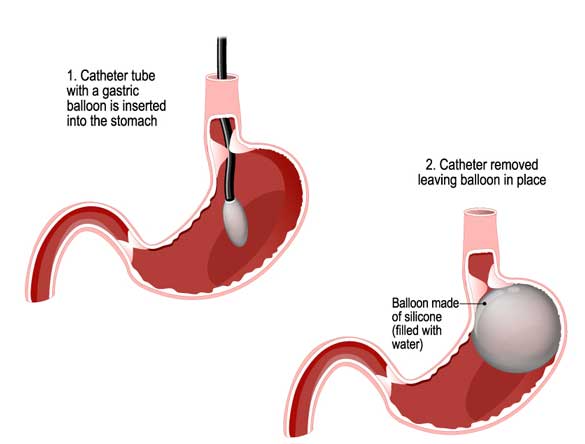
What it is: An intragastric balloon is a type of restrictive weight loss surgery in which a deflated balloon is placed in the stomach (through the mouth). Once in place, it is filled with saline solution that provides a sense of fullness, thereby curbing hunger. The intragastric balloon is not meant for people who’ve had weight loss surgery or who have bowel disease or liver failure.
Pros: There’s no surgery involved and no hospital stay required. The balloon is temporary; it stays in place for six months. A person can lose about 10 percent of his excess body weight during that time.
Cons: Possible stomachache, nausea and vomiting a few days after placement of the balloon.
Risks: The FDA in 2017 reported five deaths that may have been caused by the intragastric balloons (e.g., perforation of the stomach or esophagus, or intestinal obstruction).The agency also received multiple reports of spontaneous balloon overinflation, either with air or fluid, and acute pancreatitis caused by the balloon pressing on surrounding organs.
Summary- This is a more commonly used and a minimal procedure surgery. This is a reversible surgery and is used with patients which are having trouble with diet restrictions and physical exercise due to some medical conditions or limitations.
The ideal weight loss surgery depends on your health and body type.
For instance, if you are very obese, or if you have had abdominal surgery before, simpler surgeries might not be possible. Talk with your doctor about the pros and cons of each procedure.
If possible, go to a medical center that specializes in weight loss surgery. Studies show that complications are less likely when weight loss surgery is done by experts.
No matter where you are, always make sure that your surgeon has had plenty of experience doing the procedure you need.
Summary To choose the best weight loss surgery for you please consult a certified physician who can guide you with your BMI and provide you the best medical procedure for your body type and obesity condition.
Reference: