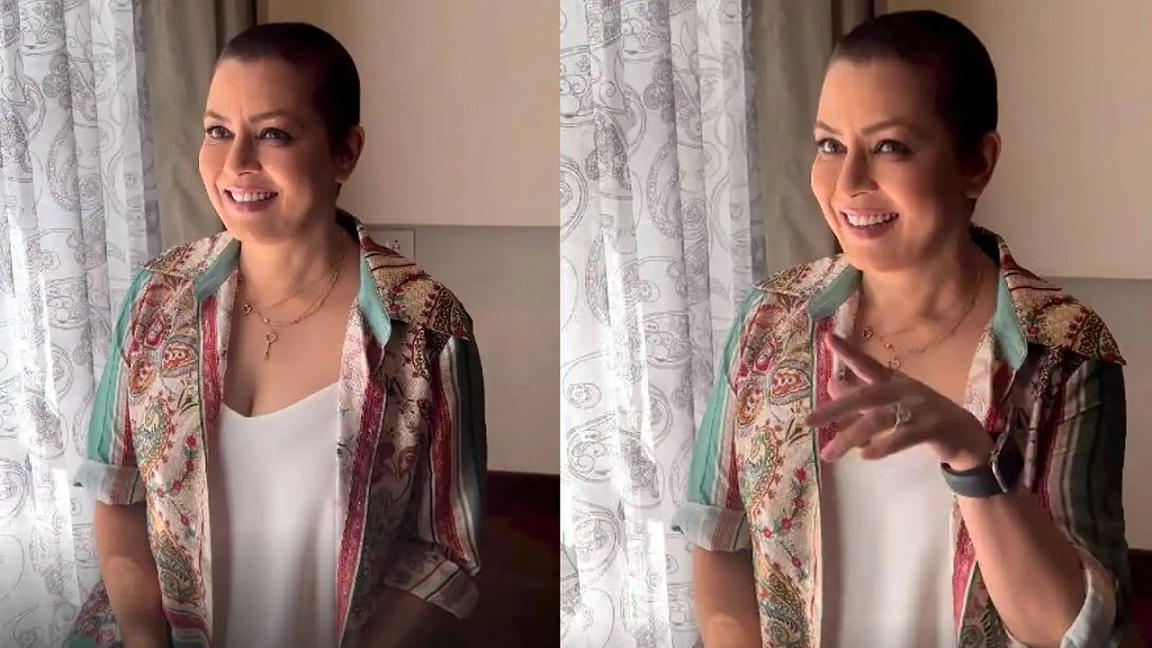Patient Testimonial, Cancer Survivor, Gallbladder cancer Surgery, Gallbladder Carcinoma, Patient Surgery
She was blessed for miraculous recovery from Advanced Stage 4 Gallbladder Cancer
While being diagnosed with cancer can be hard for a patient as well as their loved ones, here we want to share a patient’s story that will definitely give you hope that miracles can happen.
Miracles can happen.
In 2019, at the age of 53, Mrs. Veenaben Parmar was diagnosed by Dr. Kavesh Patel at Care Hospital, Himmatnagar (Gujarat) with gall bladder carcinoma (cancer) with metastasis to local and cervical lymph nodes, a stage 4 disease.
The prognosis did not look promising. As disheartening as it was to be diagnosed with stage 4 cancer, the patient and her family did not give up and decided to undergo chemotherapy.
After undergoing chemotherapy for 6 months, she continued with her oral chemotherapy(chemo drugs taken by mouth).
As it is a known fact that Metastatic Gallbladder Cancer has poor prognosis, the one year survival rate with distant metastasis is hardly possible, the patient had consulted many oncologists but was disappointed with poor survival facts. After going through the cancer treatment for many months and learning about the poor survival rates, the patient decided to stop with her treatment plans altogether.
For the next two years, she neither consulted any general doctor or a cancer specialist regarding her health. She did not follow up to check whether her condition had worsened or if it was the same.
Then in Nov 2022, Mrs. Parmar was diagnosed with acute cholecystitis.
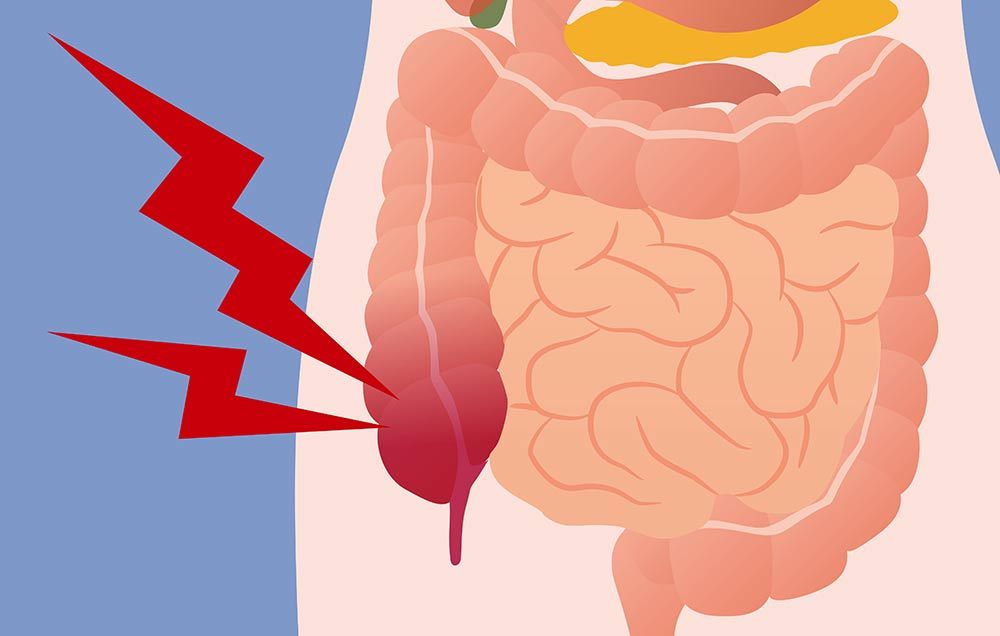
Acute cholecystitis is swelling (inflammation) of the gallbladder. It is a potentially serious condition that usually needs to be treated in hospital. The main symptom of acute cholecystitis is a sudden sharp pain in the upper right side of your tummy (abdomen) that spreads towards your right shoulder
On further evaluation by PET scan, it was discovered that she only had local disease and that the distant metastasis, which was previously diagnosed in 2019, was cleared. This is a very rare happening and in this case the patient was unaware that she had responded positively to the chemotherapy.
Following this positive news, the patient was offered a complete surgical cure.
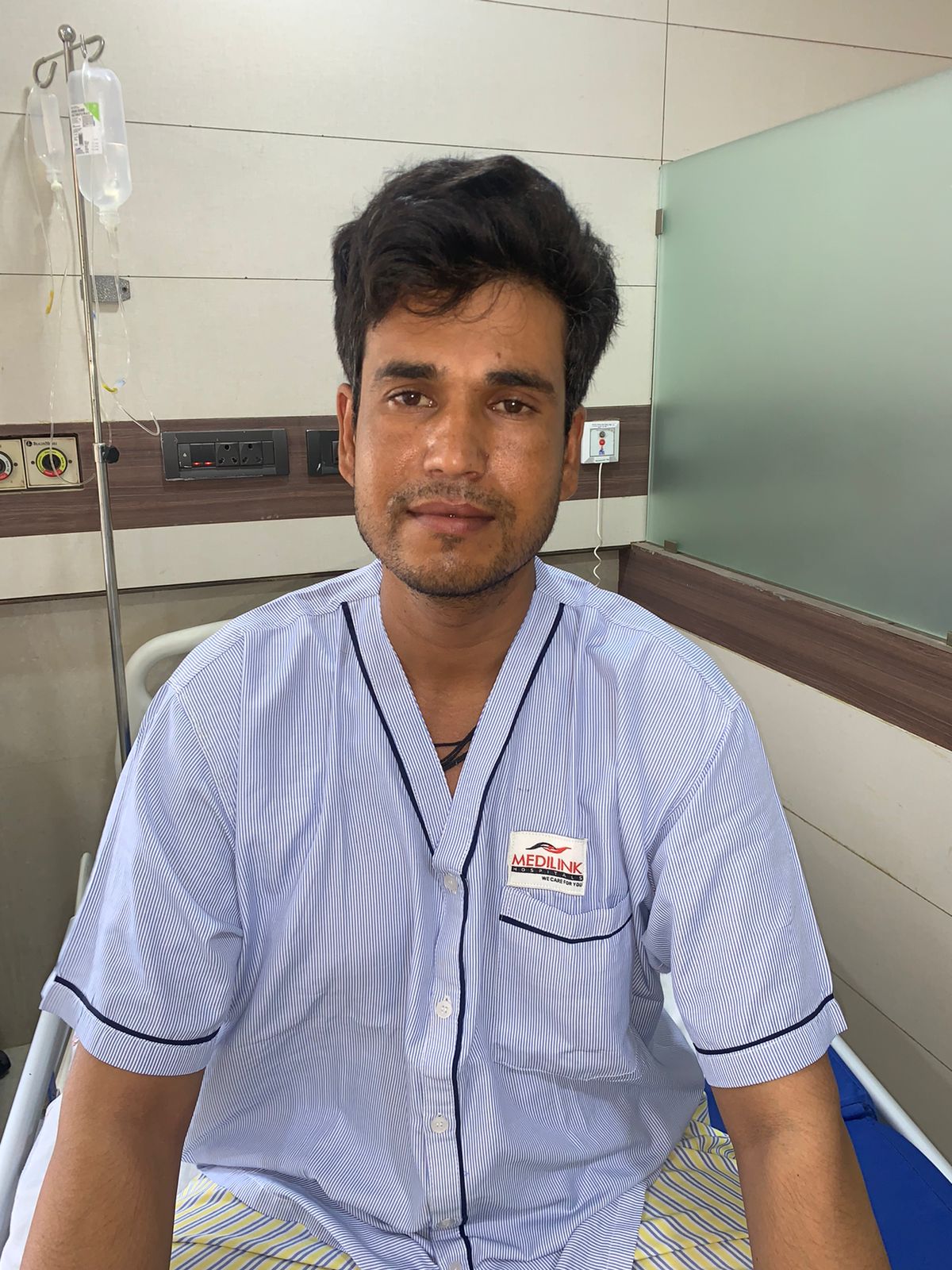
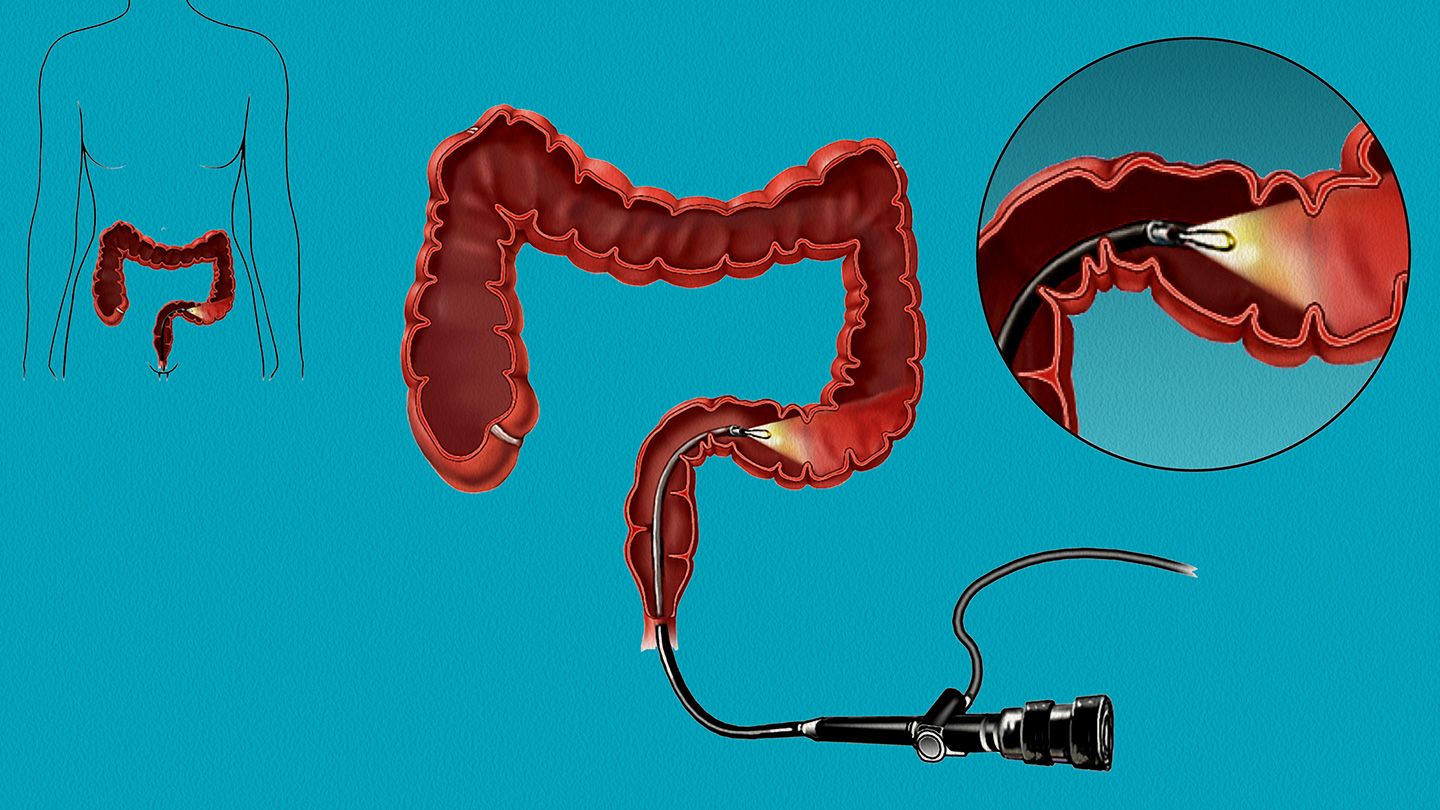
Mrs. Veenaben Parmar then underwent extended (radical) cholecystectomy and was operated by Dr. Avinash Tank (Liver Surgeon) & Dr. Kavesh Patel at Prime Hospital, Himatnagar, Gujarat.
Extended (radical) cholecystectomy- An extended cholecystectomy removes: The gallbladder. About an inch or more of liver tissue next to the gallbladder. All of the lymph nodes in the region. The extent of the surgery depends on where the cancer is and how far it might have spread.
The surgery went well. The patient was discharged on the 7th day from the day of operation after being kept under observation for almost a week when there were no further complications.
It is already a miracle that a stage 4 cancer patient survived for 3 years including the 2 years where she did not receive any treatment and by Nov 2022, she had reached an operable stage where surgery was possible to remove the tumour.
We are hoping for the best for Mrs. Parmar and wish her happy, healthy and cancer free life ahead.
We are glad to say that Liver resection surgery is now possible at Prime Hospital, Himmatnagar (Gujarat).
About Gallbladder cancer
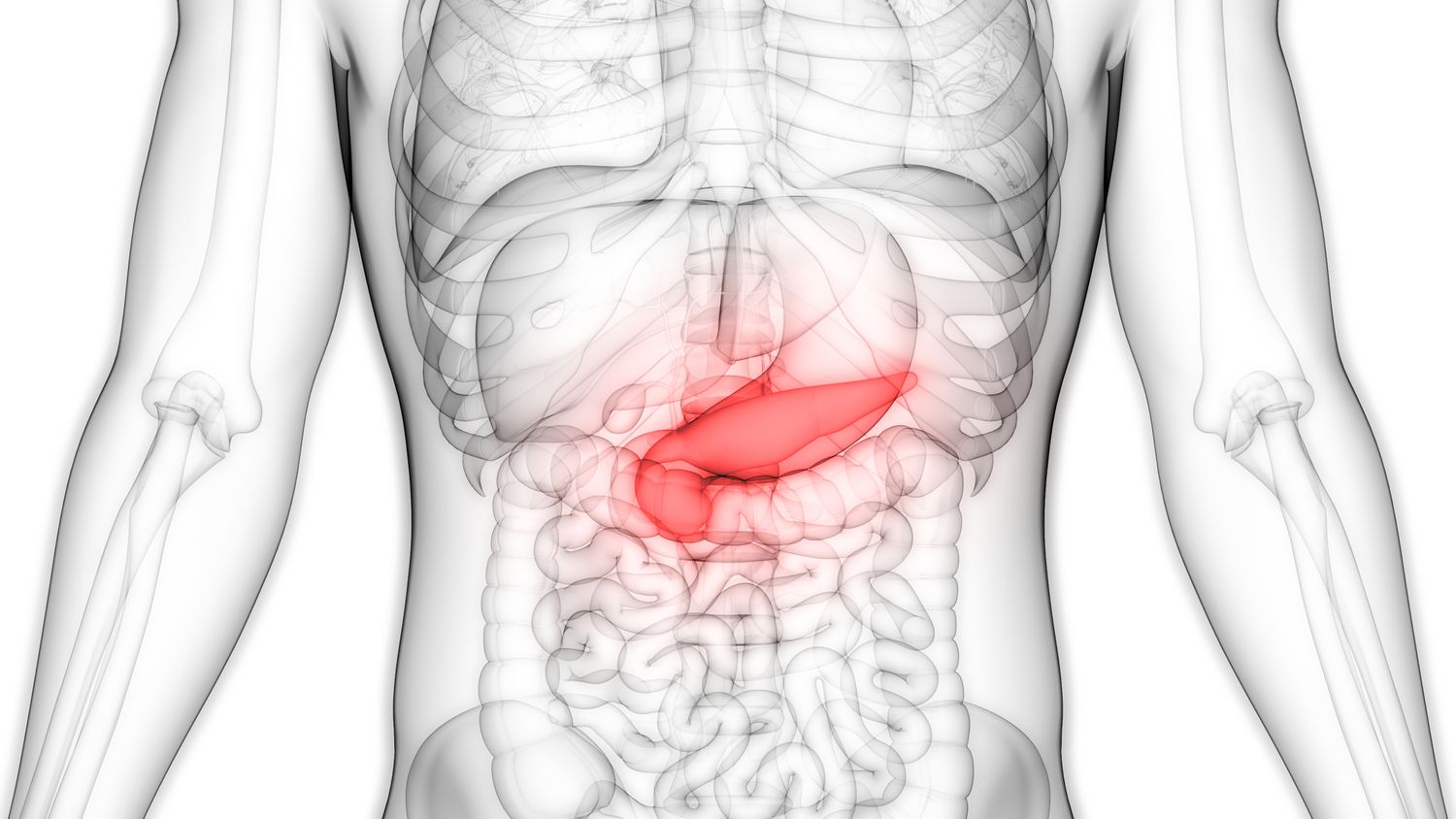
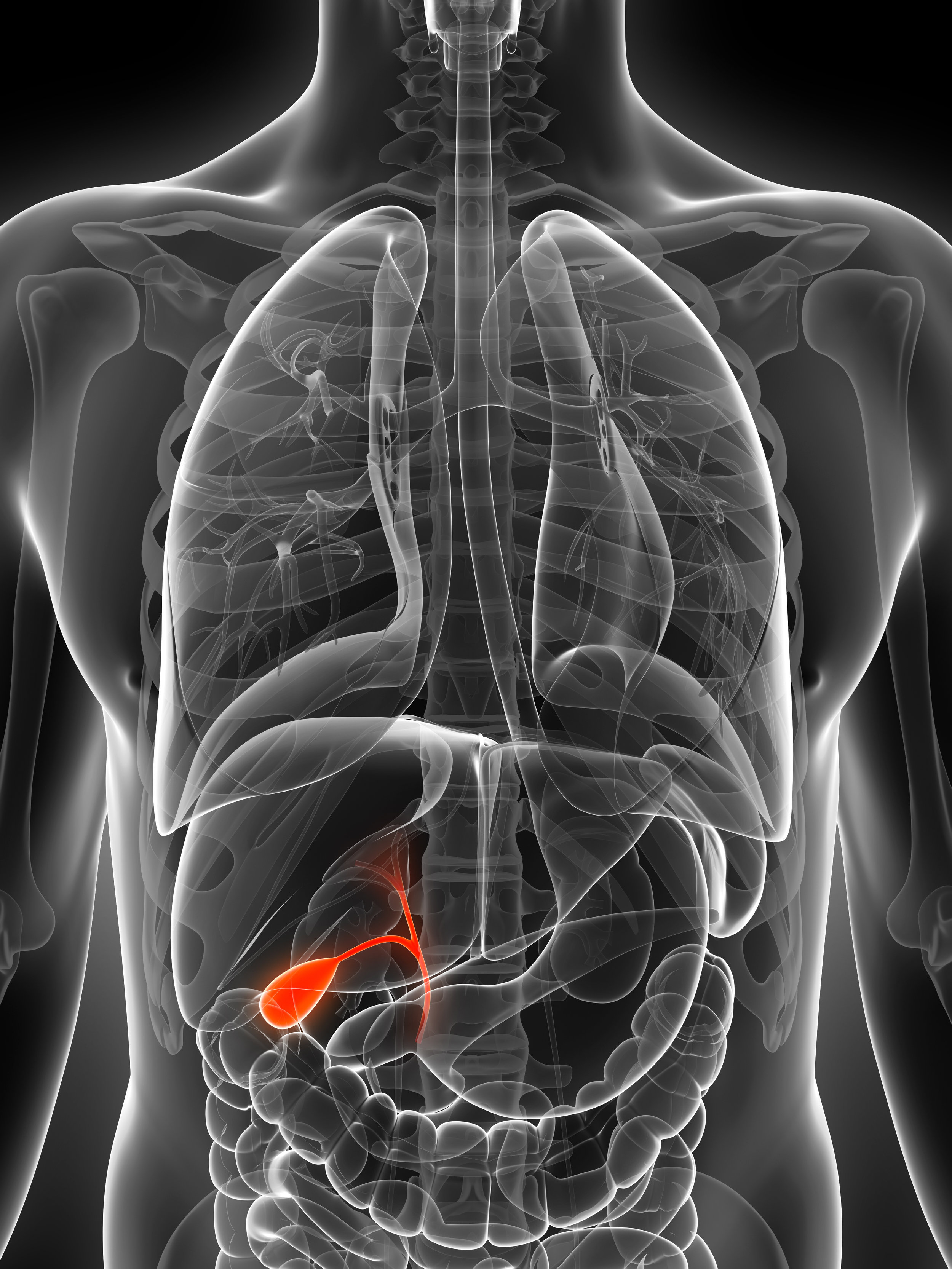
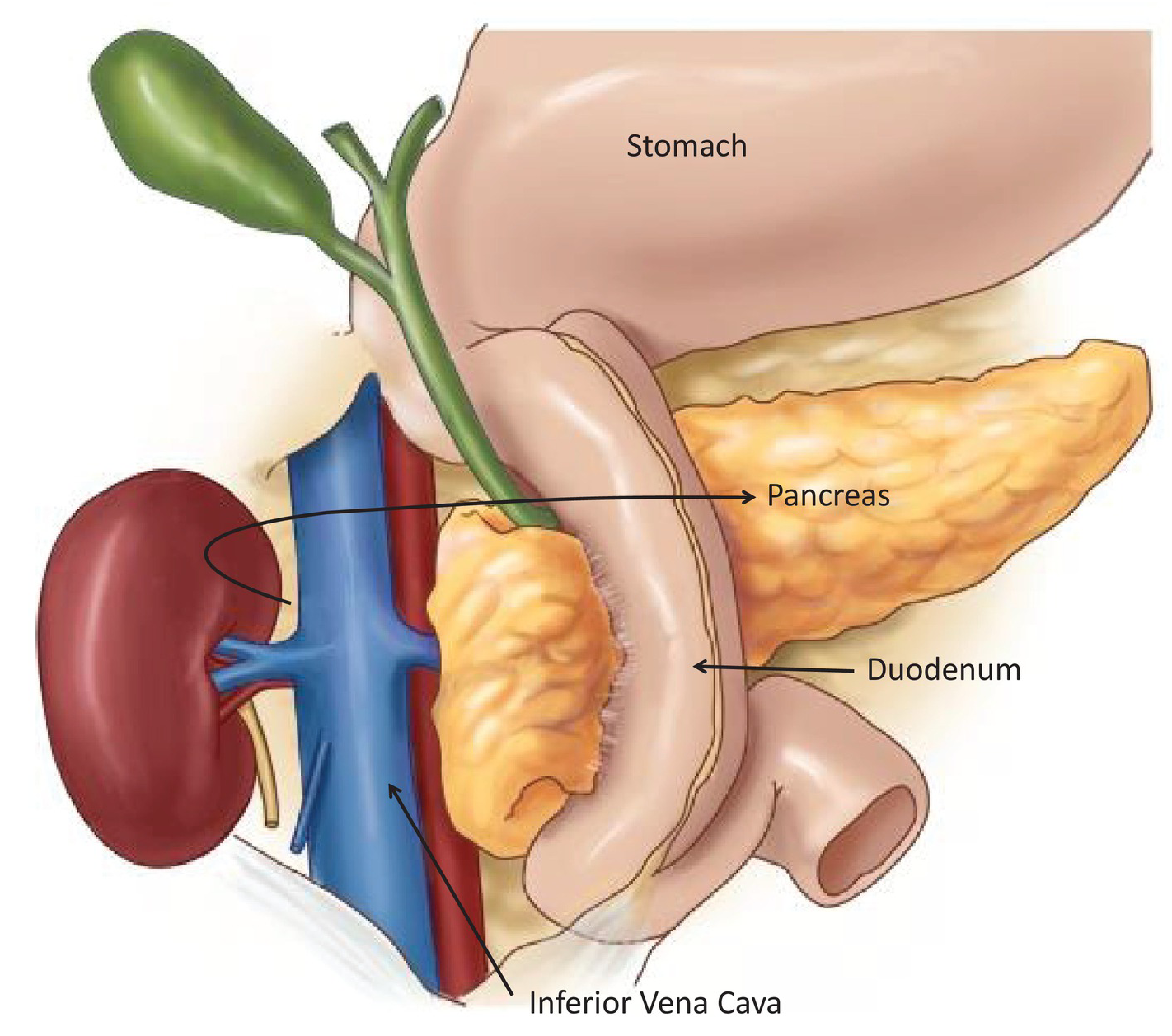
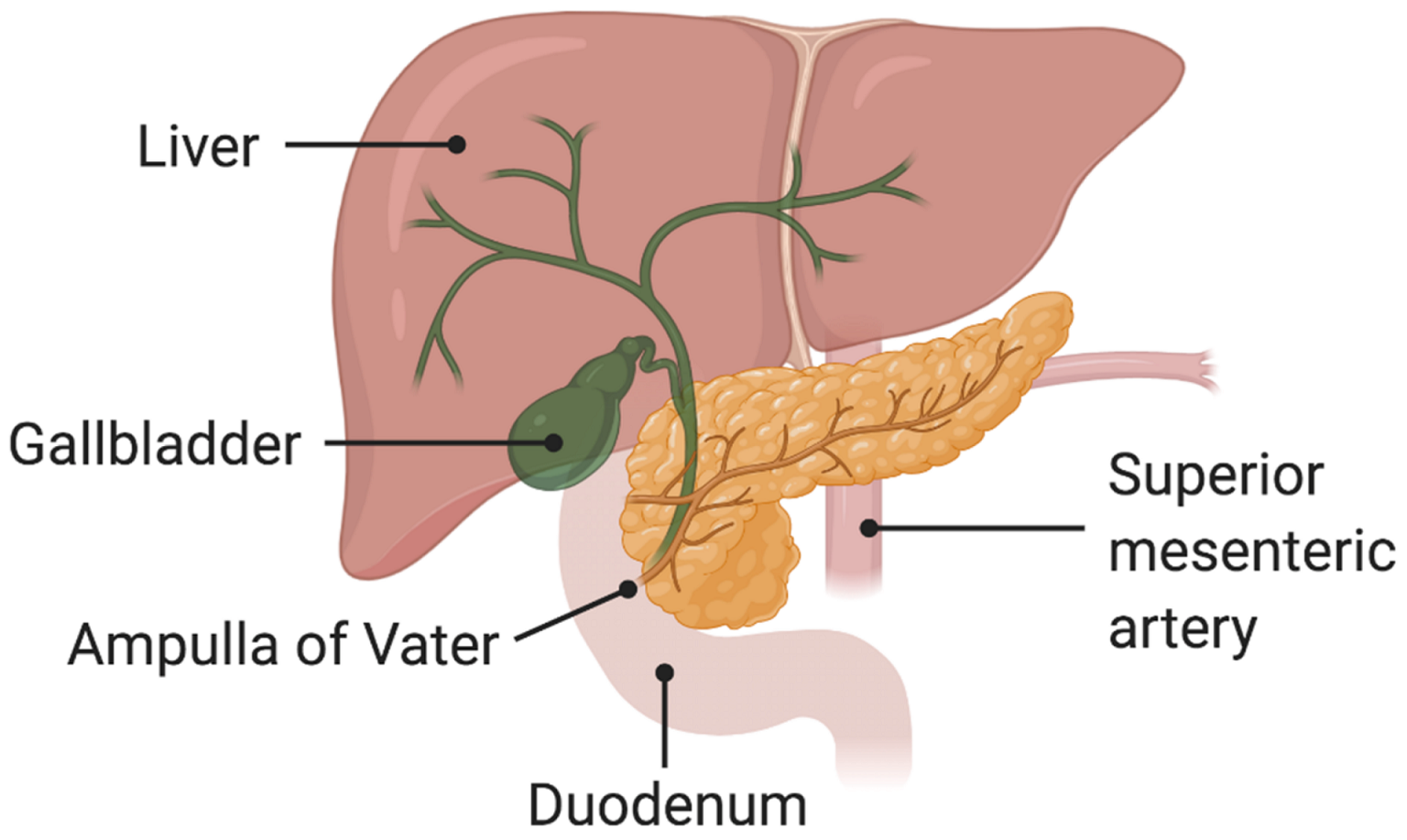
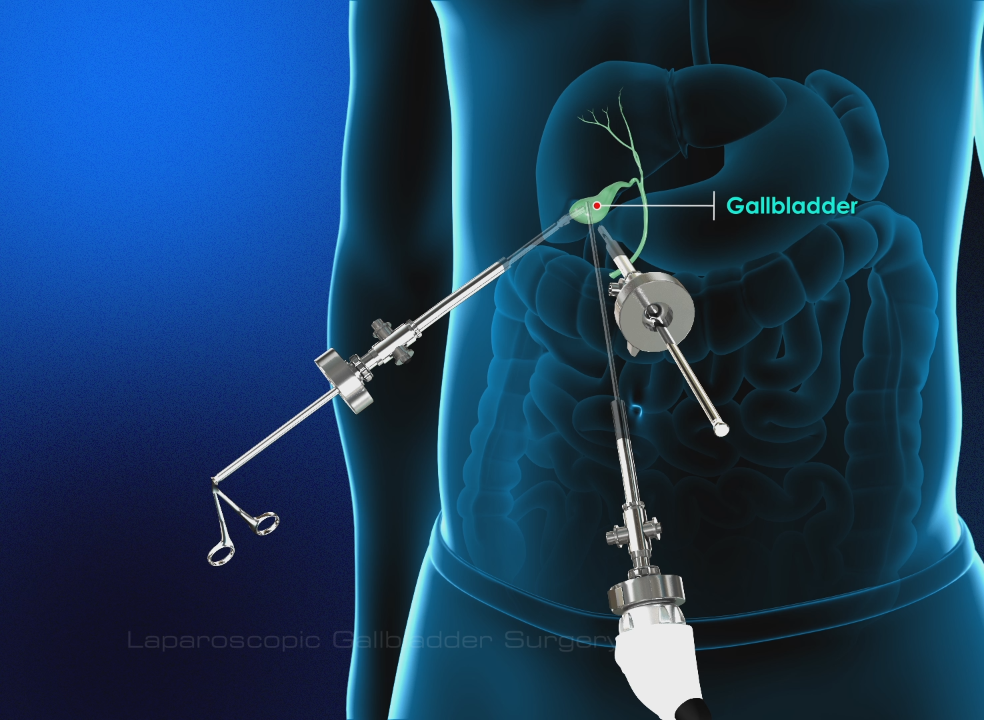
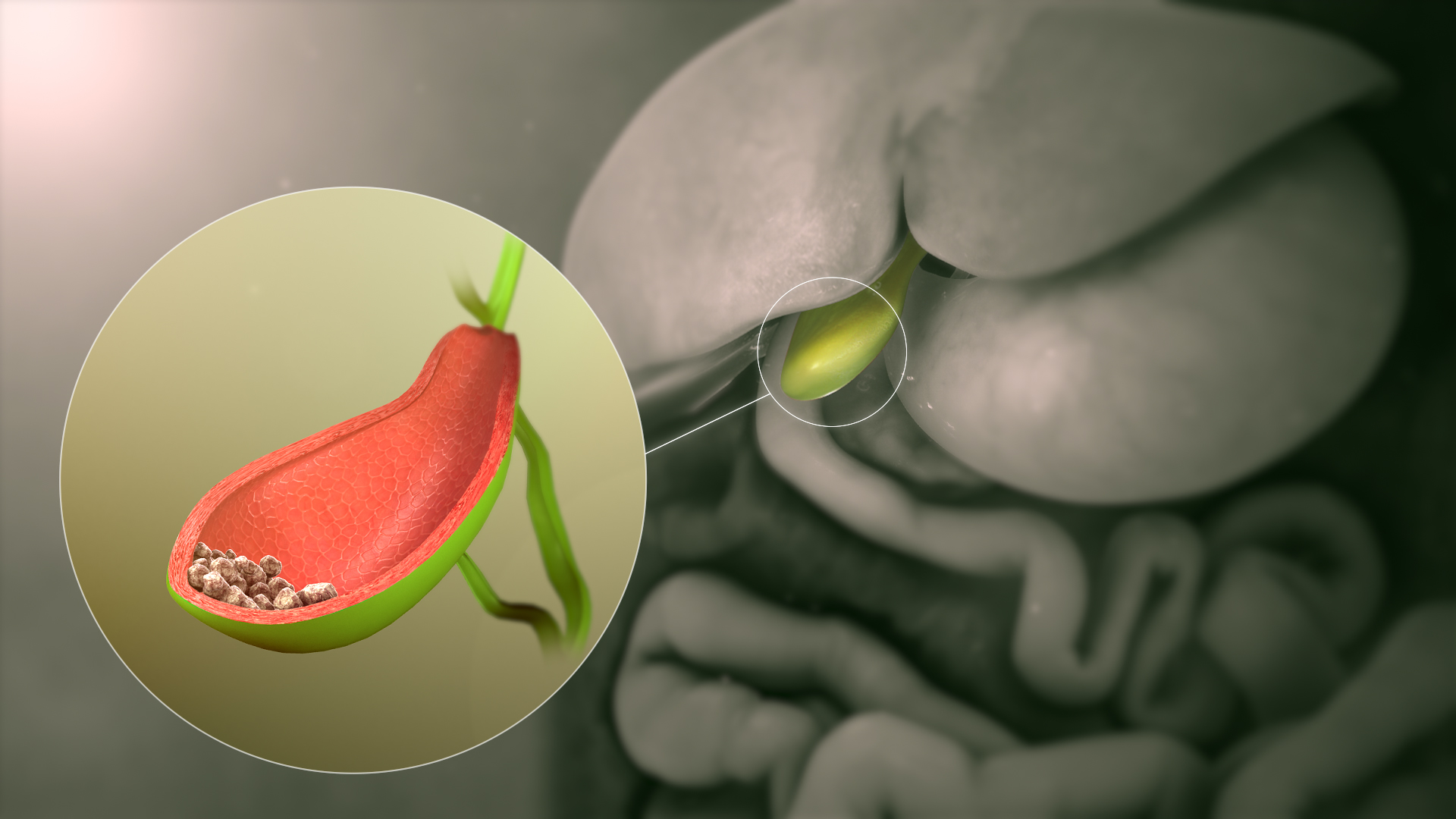
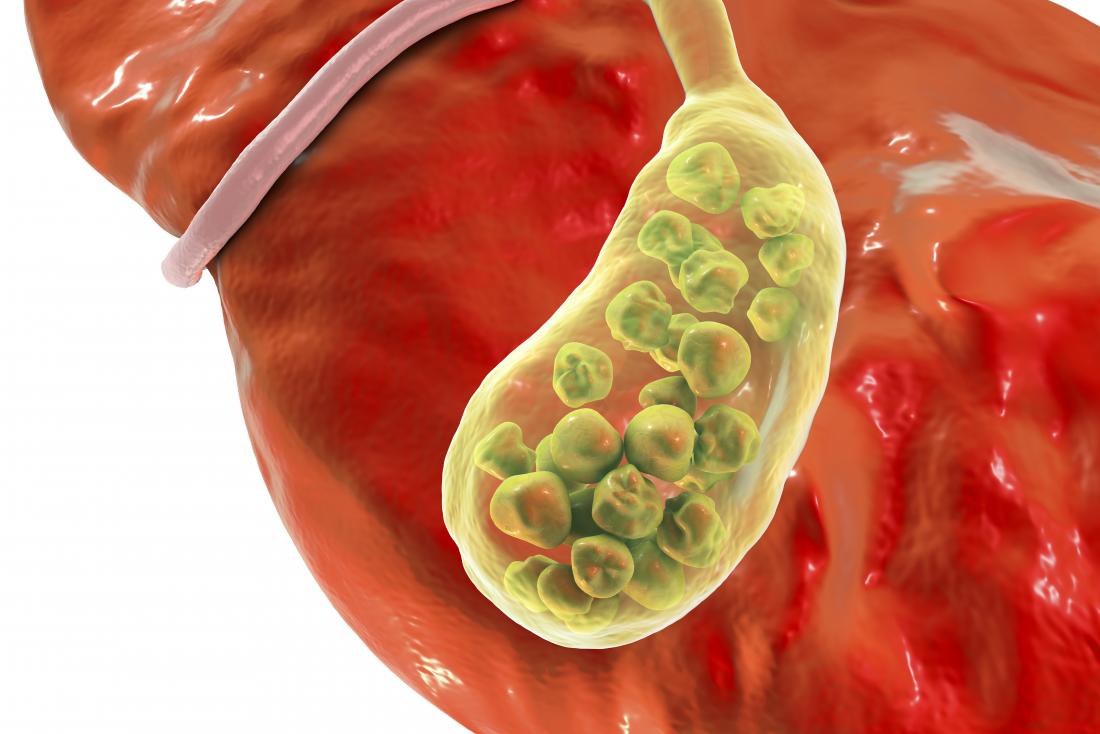
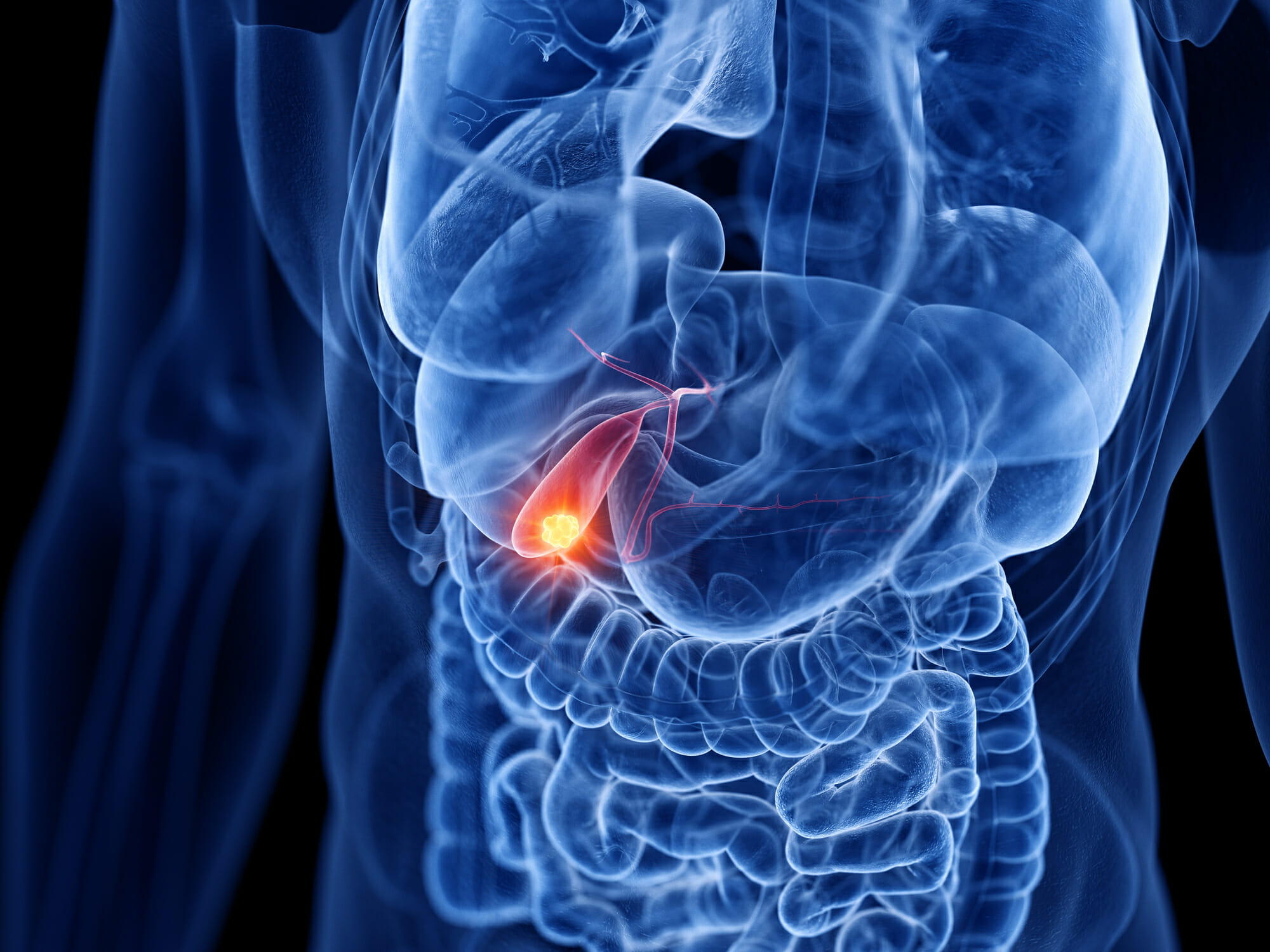
What is Gallbladder?
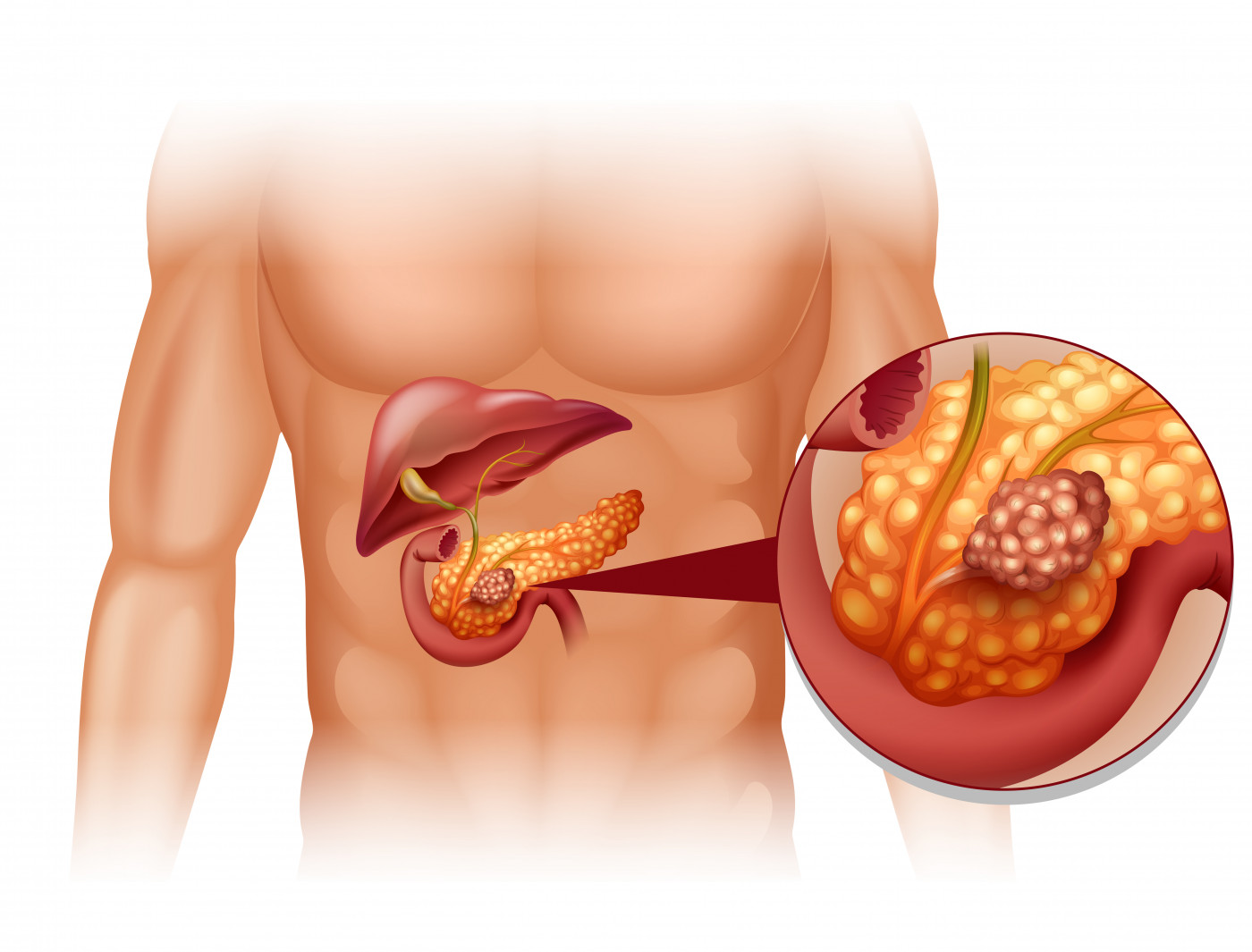
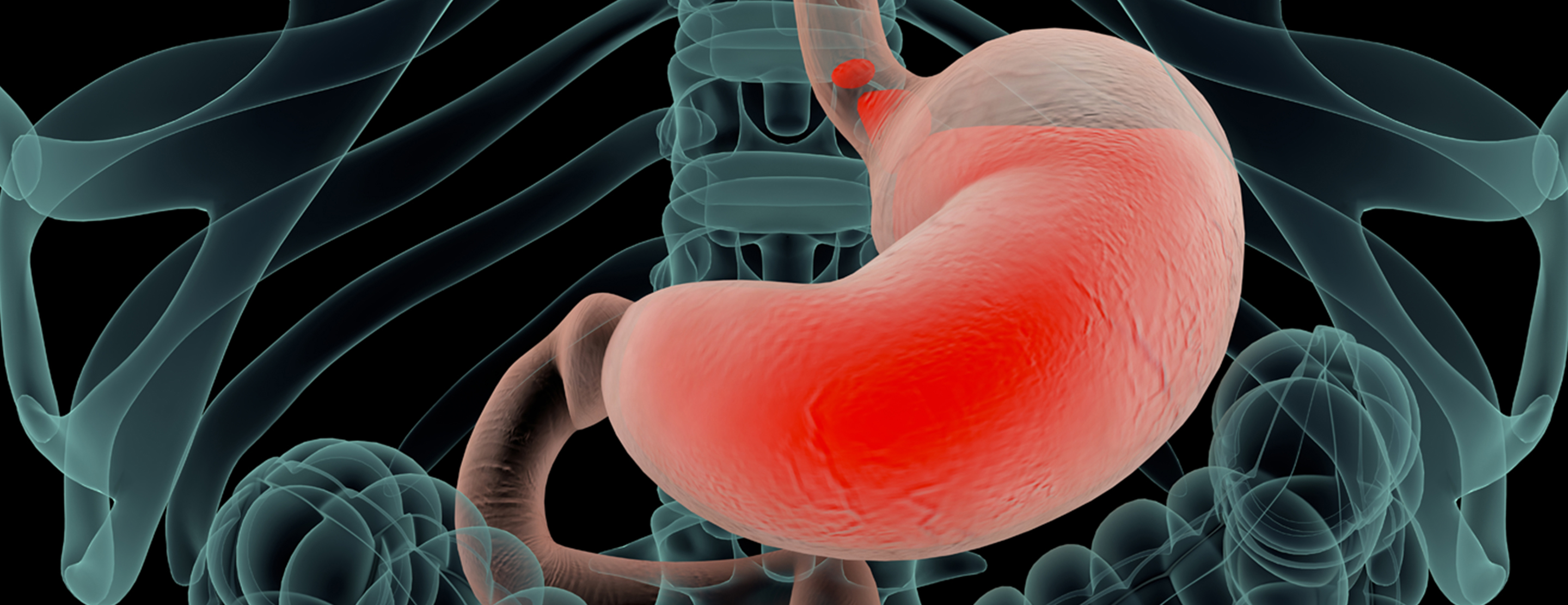
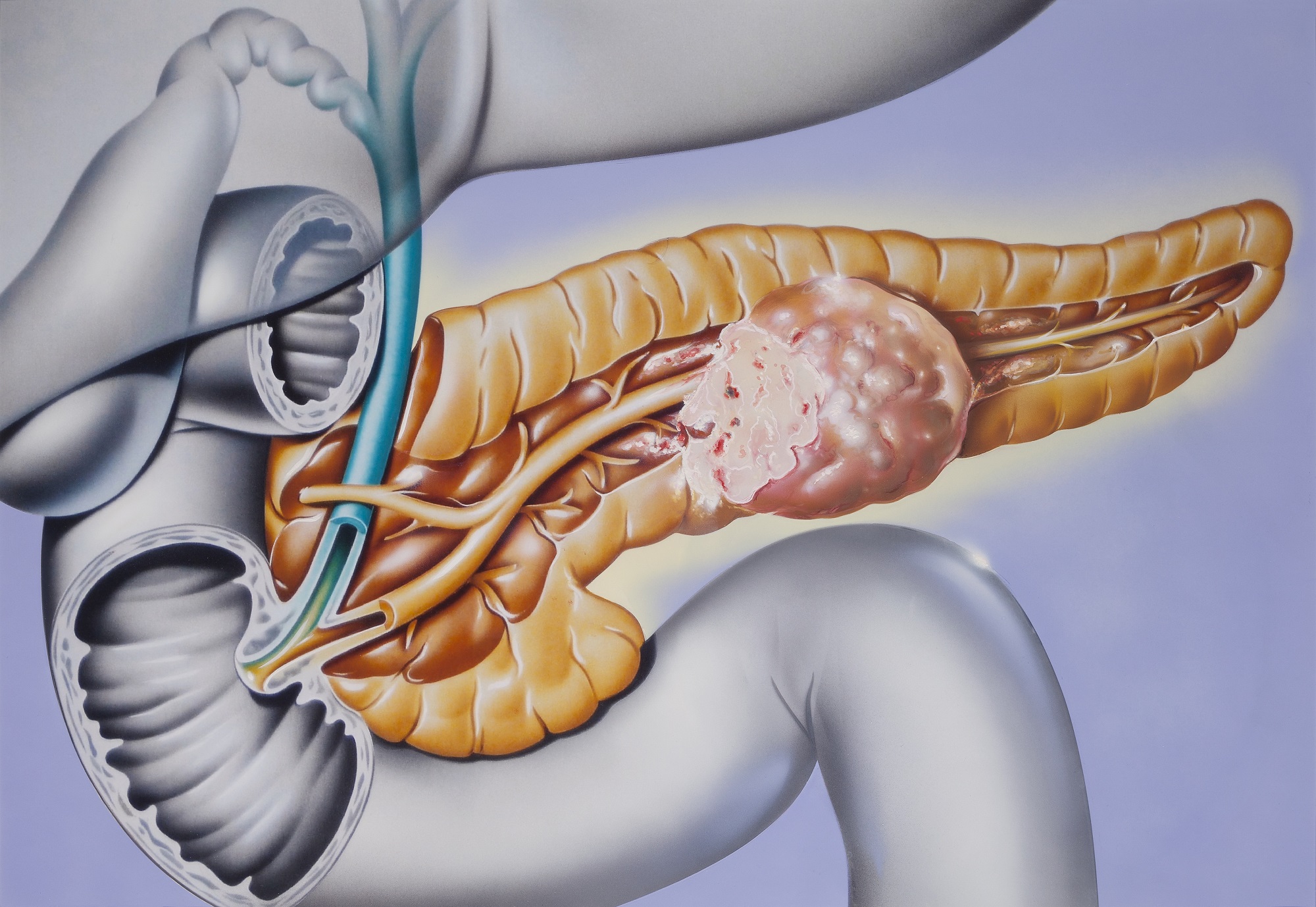
Gallbladder cancer is an abnormal growth of cells that begins in the gallbladder.
Your gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of your abdomen, just beneath your liver. The gallbladder stores bile, a digestive fluid produced by your liver.
Gallbladder cancer is uncommon. When gallbladder cancer is discovered at its earliest stages, the chance for a cure is very good. But most gallbladder cancers are discovered at a late stage, when the prognosis is often very poor.
Gallbladder cancer may not be discovered until it's advanced because it often causes no specific signs or symptoms. Also, the relatively hidden nature of the gallbladder makes it easier for gallbladder cancer to grow without being detected.
Symptoms
Gallbladder cancer signs and symptoms may include:
- Abdominal pain, particularly in the upper right portion of the abdomen
- Abdominal bloating
- Losing weight without trying
- Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)
When to see a doctor
Make an appointment with your doctor if you experience any signs or symptoms that worry you
Causes
It's not clear what causes gallbladder cancer.
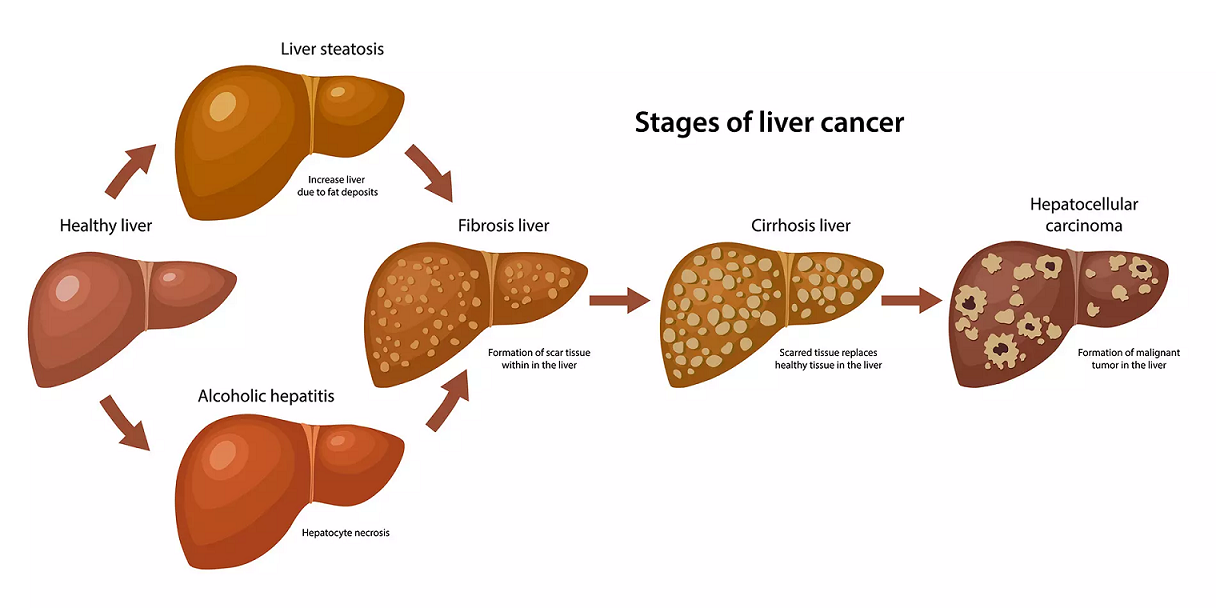
Doctors know that gallbladder cancer forms when healthy gallbladder cells develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell's DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do. The changes tell the cells to grow out of control and to continue living when other cells would normally die. The accumulating cells form a tumour that can grow beyond the gallbladder and spread to other areas of the body.
Most gallbladder cancer begins in the glandular cells that line the inner surface of the gallbladder. Gallbladder cancer that begins in this type of cell is called adenocarcinoma. This term refers to the way the cancer cells appear when examined under a microscope.
Risk factors
Factors that can increase the risk of gallbladder cancer include:
- Your sex. Gallbladder cancer is more common in women.
- Your age. Your risk of gallbladder cancer increases as you age.
- A history of gallstones. Gallbladder cancer is most common in people who have gallstones or have had gallstones in the past. Larger gallstones may carry a larger risk. Still, gallstones are very common and even in people with this condition, gallbladder cancer is very rare.
- Other gallbladder diseases and conditions. Other gallbladder conditions that can increase the risk of gallbladder cancer include polyps, chronic inflammation and infection.
- Inflammation of the bile ducts. Primary sclerosing cholangitis, which causes inflammation of the ducts that drain bile from the gallbladder and liver, increases the risk of gallbladder cancer.
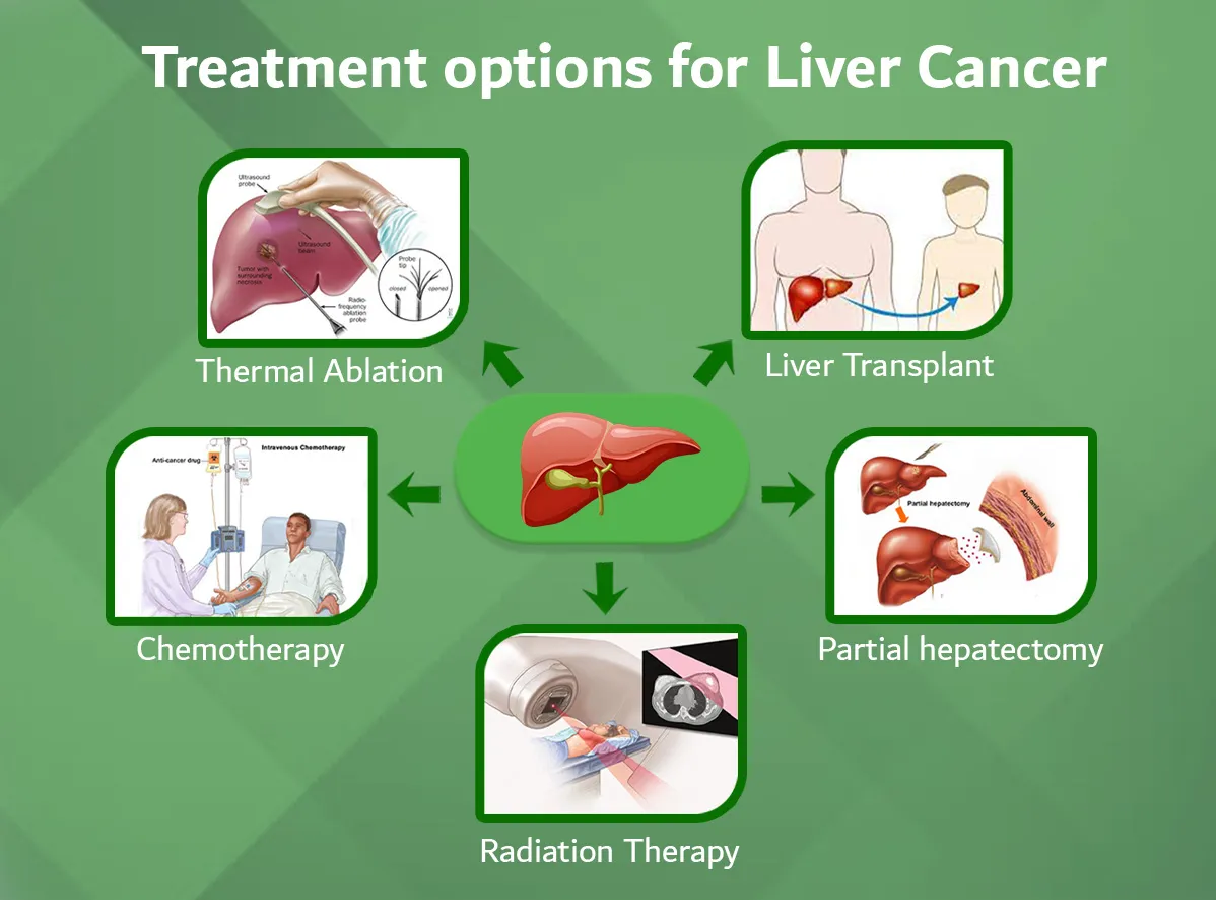
Gallbladder Cancer Treatment
The treatment for Gallbladder Cancer depends on the age and general health of the patient and whether the cancer is causing symptoms.
Gallbladder cancer can be cured only if it is found before it has spread, when it can be removed by surgery. If the cancer has spread, palliative treatment can improve the patient's quality of life by controlling the symptoms and complications of this disease
Three types of standard treatment are used:
Surgery
Gallbladder cancer may be treated with a Cholecystectomy, surgery to remove the gallbladder and some of the tissues around it. Nearby lymph nodes may be removed. A laparoscope is sometimes used to guide gallbladder surgery. The laparoscope is attached to a video camera and inserted through an incision (port) in the abdomen. Surgical instruments are inserted through other ports to perform the surgery. Because there is a risk that gallbladder cancer cells may spread to these ports, tissue surrounding the port sites may also be removed. If the cancer has spread and cannot be removed, the following types of palliative surgery may relieve symptoms:
- Surgical biliary bypass: If the tumor is blocking the small intestine and bile is building up in the gallbladder, a biliary bypass may be done. During this operation, the gallbladder or bile duct will be cut and sewn to the small intestine to create a new pathway around the blocked area.
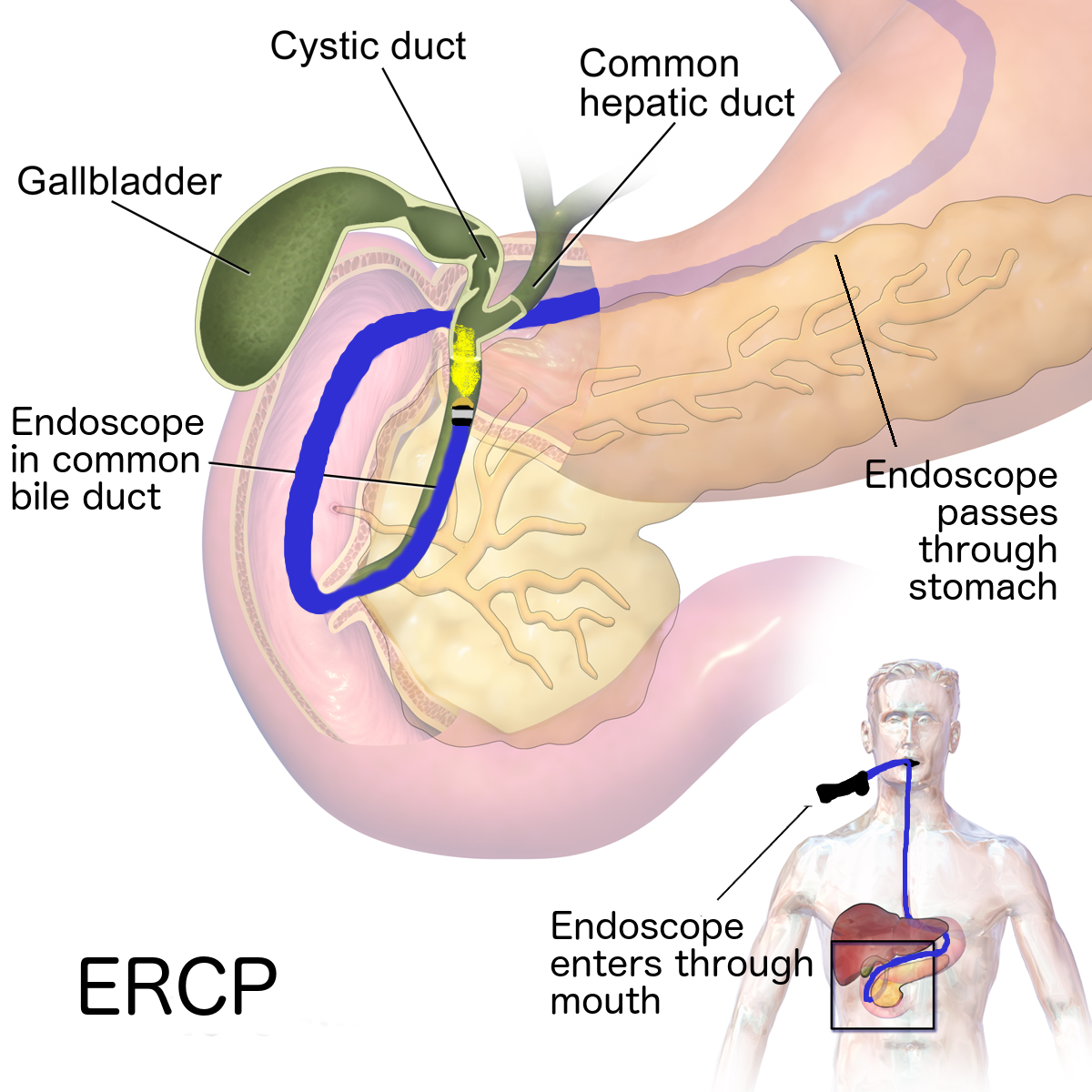
- Endoscopic stent placement: If the tumor is blocking the bile duct, surgery may be done to put in a stent (a thin, flexible tube) to drain bile that has built up in the area. The stent may be placed through a catheter that drains to the outside of the body or the stent may go around the blocked area and drain the bile into the small intestine.
- Percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage: A procedure done to drain bile when there is a blockage and endoscopic stent placement is not possible. An x-ray of the liver and bile ducts is done to locate the blockage. Images made by ultrasound are used to guide placement of a stent, which is left in the liver to drain bile into the small intestine or a collection bag outside the body. This procedure may be done to relieve jaundice before surgery.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells. There are two types of radiation therapy. External radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to send radiation toward the cancer. Internal radiation therapy uses a radioactive substance sealed in needles, seeds, wires, or catheters that are placed directly into or near the cancer. The way the radiation therapy is given depends on the type and stage of the cancer being treated.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping the cells from dividing. When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body (systemic chemotherapy). When chemotherapy is placed directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, an organ, or a body cavity such as the abdomen, the drugs mainly affect cancer cells in those areas (regional chemotherapy). The way the chemotherapy is given depends on the type and stage of the cancer being treated
Learn More about Gallbladder Cancer- causes, treatment, post operative care and more here.