Fatty Liver, Medical News
Fatty Liver on the rise in Urban and Rural population in the country- Latest survey reports
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease ( NAFLD) is presently the most prevalent cause of liver disease in the world. NAFLD affects about 25% of the global adult population. The prevalence of NAFLD in India is about 9% to 32%.
About the Survey
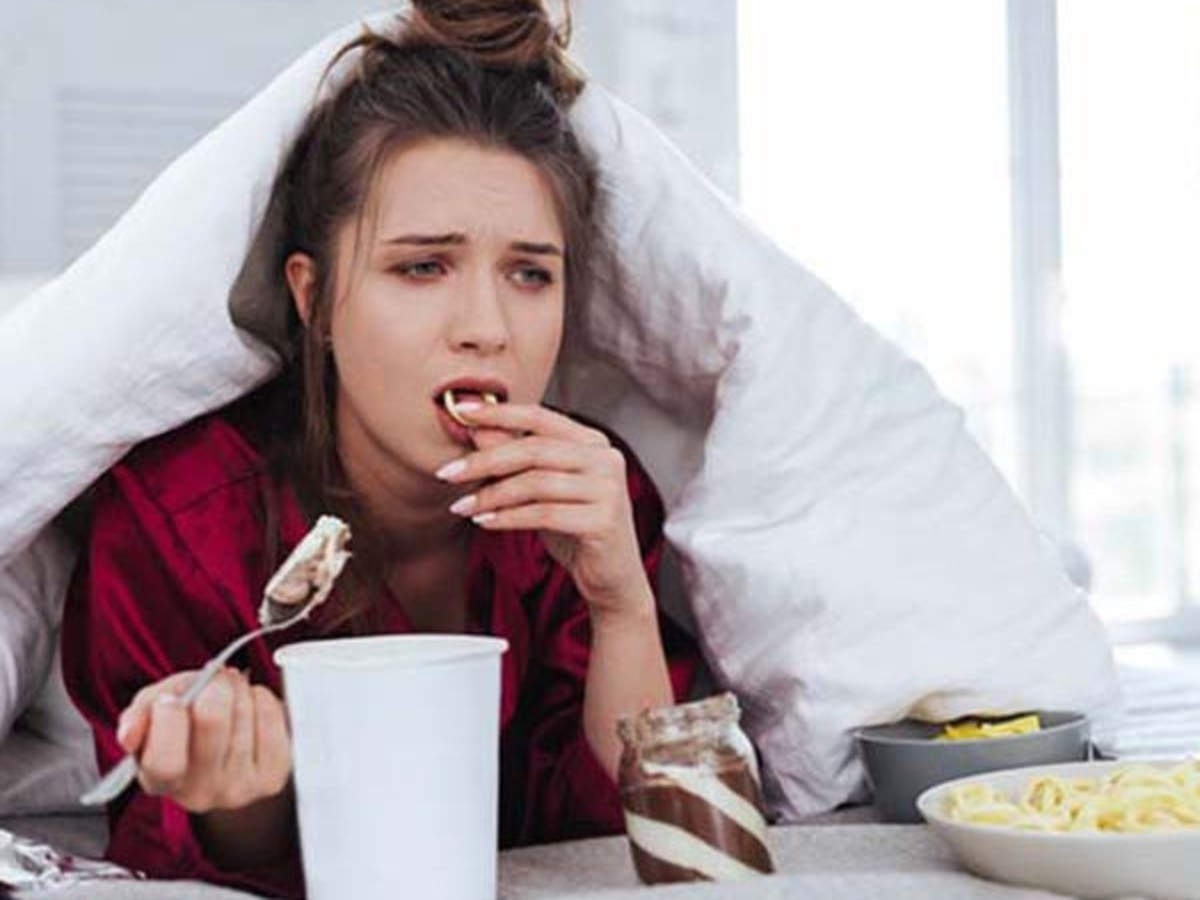
Sedentary lifestyle, poor dietary habits resulting in obesity, uncontrolled diabetes and hypertension are leading to significant increase in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) among people in urban and rural areas, a door-to-door survey taken-up by doctors from Hyderabad-based Asian Institute of Gastroenterology (AIG), said.
More than 25 per cent of people in urban areas and 20 per cent in rural areas have fatty liver disease, the findings from AIG’s rural outreach program taken up in Telangana, has indicated. The clinical data from the survey has shown that 4 out of 10 people might have fatty liver disease. (Source)
“NAFLD is becoming an epidemic in our country because of sedentary lifestyle and poor dietary habits. The concerning factor is that NAFLD doesn’t show many symptoms and therefore it is mainly diagnosed incidentally. We are conducting our rural outreach program with an objective to screen the rural population for various GI diseases for which we do abdominal ultrasound in rural areas. Surprisingly, close to 20 per cent of the scans showed the presence of fatty liver,” Chairman and Chief of Gastroenterology, AIG Hospitals, said while sharing some of the incidental findings from the clinical data collected during the survey.
Researchers observed “major factors that are driving cases of fatty liver are obesity, uncontrolled diabetes and hypertension. We now know that management of fatty liver is not just about the liver but also includes effective treatment of blood sugar, hypertension and obesity.”
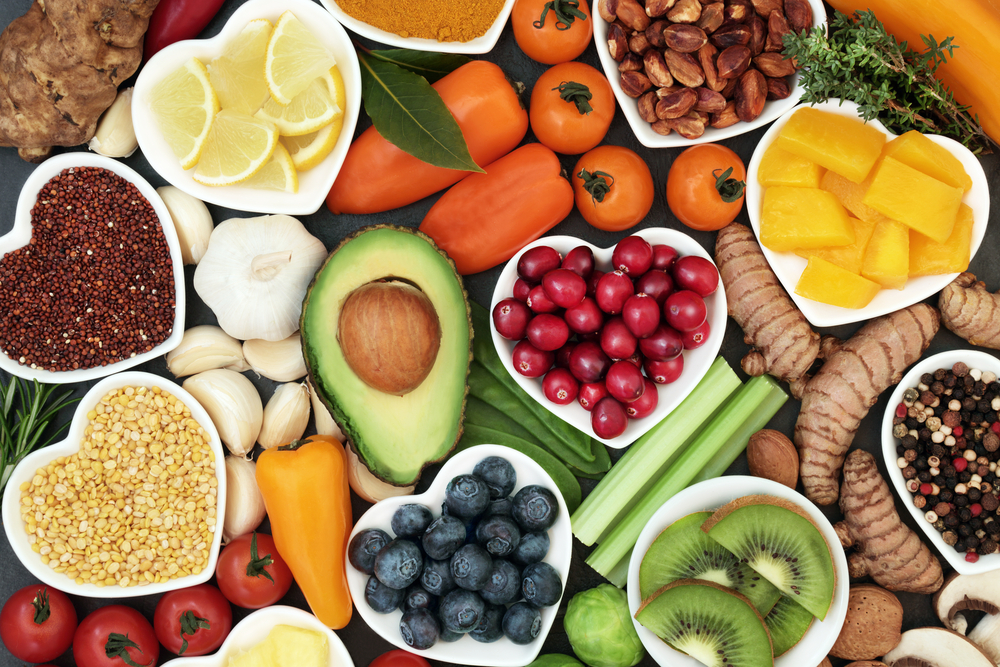
Public awareness plays a big role in combating fatty liver disease because the first line of treatment for NAFLD is weight loss, through a combination of calorie reduction, exercise, and healthy eating.
What is Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)?
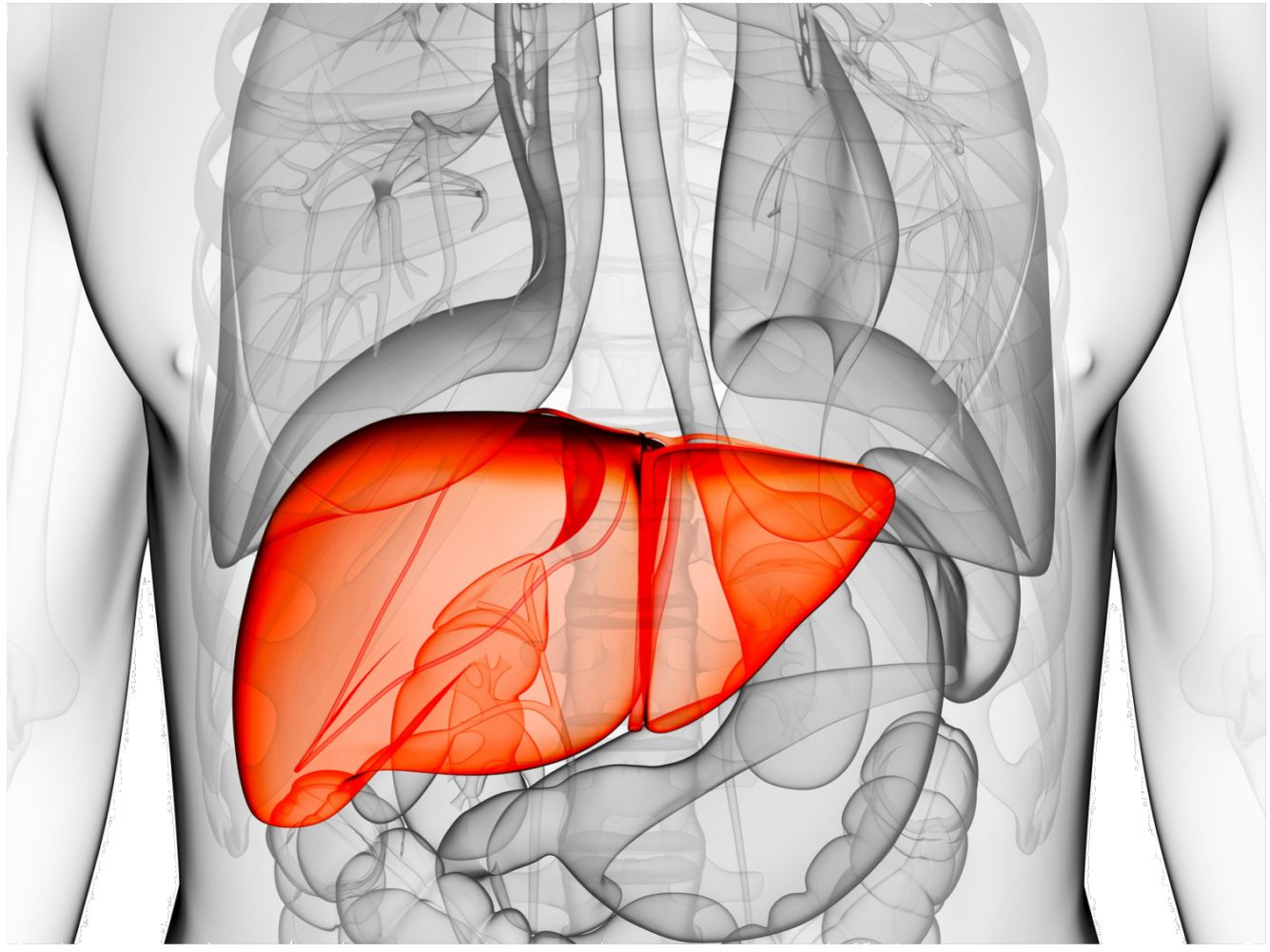
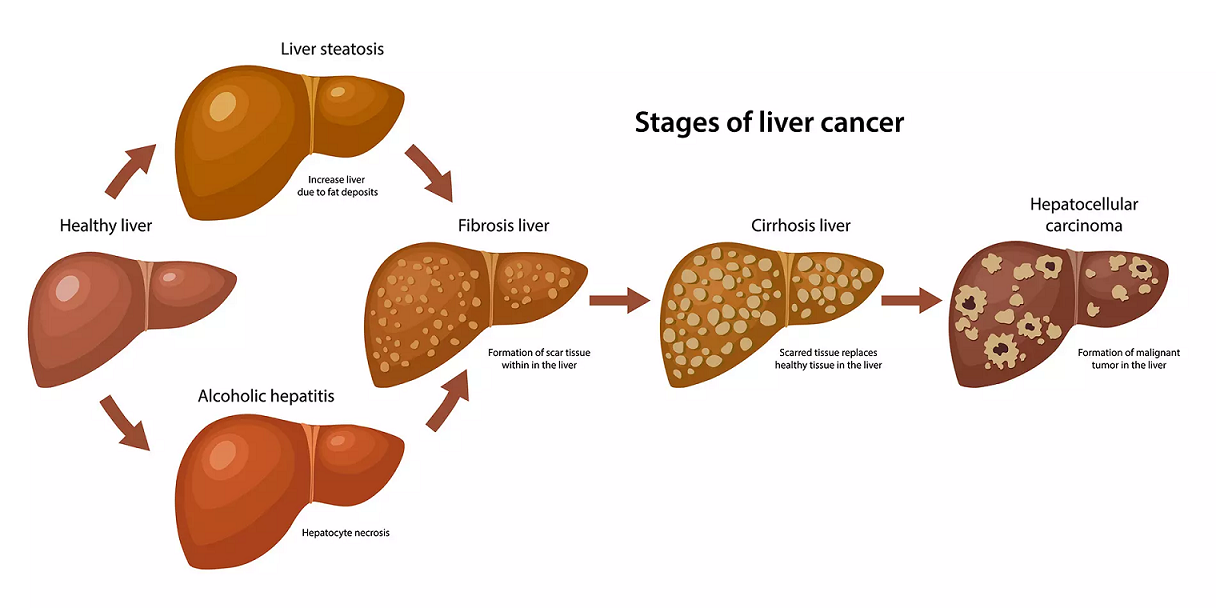
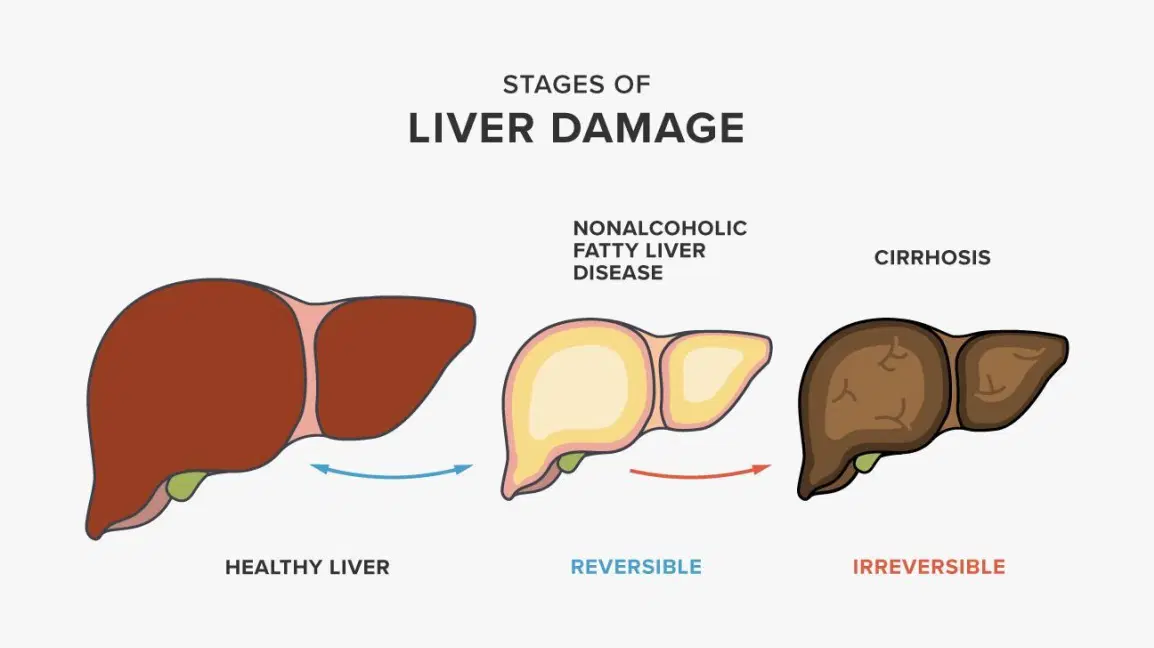
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) is a leading cause of chronic liver diseases globally. NAFLD is a medical condition in which excess fat deposits in the liver. This deposition of fat is not caused by heavy alcohol use.
NAFLD affects about 25% of the global adult population ranging from 13.5% in Africa to 31.8% in the Middle East. The prevalence of NAFLD in India is about 9% to 32%.(Source)
NAFLD can be classified into two sub categories: Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver or Simple Fatty Liver (NAFL) and Non-Alcoholic SteatoHepatitis (NASH).
- Simple fatty liver-In this condition, fat is deposited in the liver without any inflammation and liver damage and does not progress to cause complications.
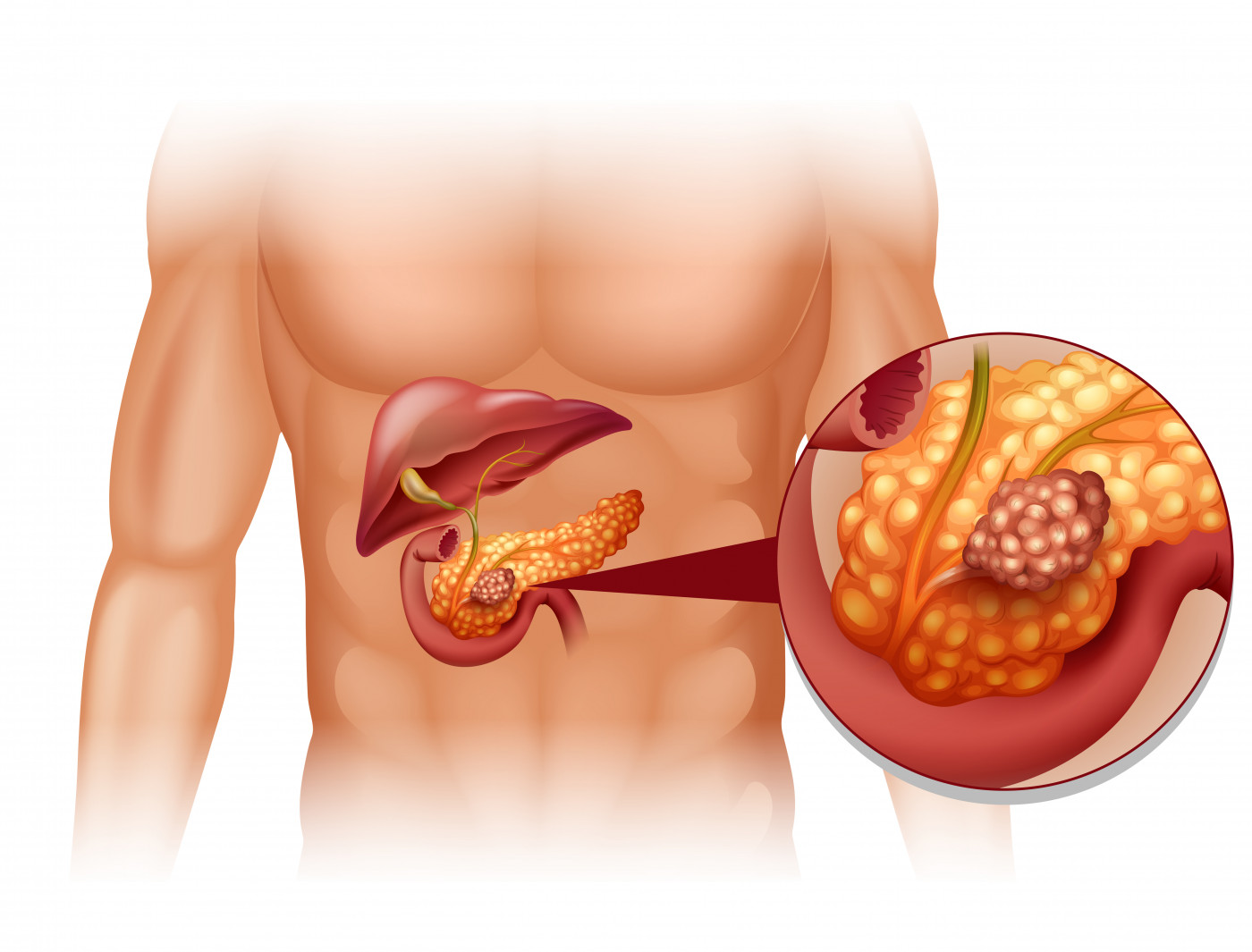
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)- In this condition, in addition to fat deposits, inflammation of liver cells is there which can cause fibrosis, or scarring of the liver and can lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer.
NAFLD Risk Factors
NAFLD can affect people of any age, including children. Several factors contribute to the development of NAFLD such as-
- Family history of NAFLD or
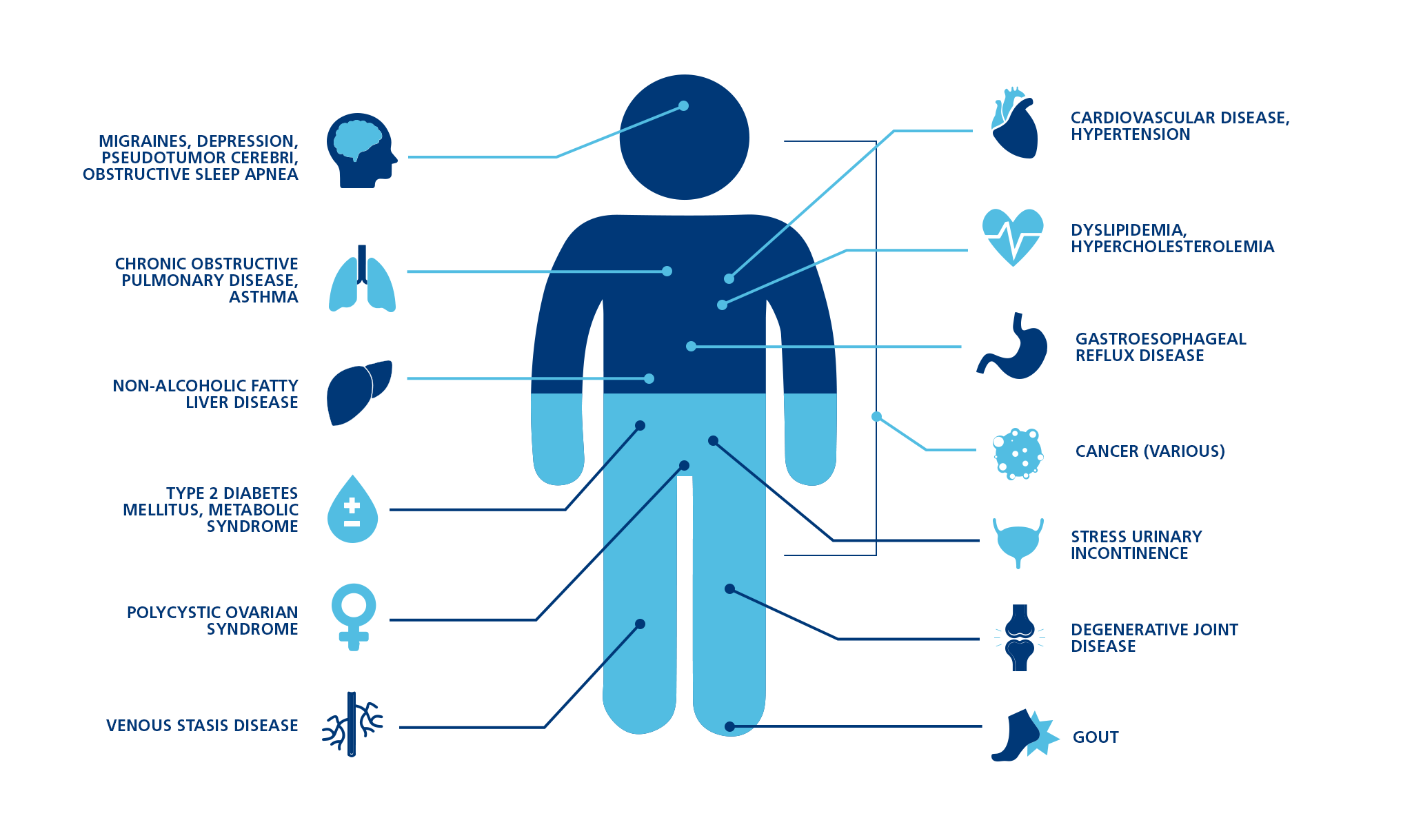
- Metabolic syndrome and environmental modifiers such as diet, lifestyle, presence of obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia.
How are fatty liver disease and diabetes-related?
Fatty liver is one of the most important factors predictive of the development of diabetes. It leads to diabetes in most individuals; as liver damage progresses due to fatty liver, insulin resistance increases which finally culminates in diabetes. Fatty liver has also been associated with an increased risk of heart problems and raised cholesterol.
Are there any other comorbidities associated with fatty liver?
Large population studies have shown that fatty liver also predisposes the individual to heart disease, cholesterol problems, hypertension and definitely diabetes. Diabetes is only the tip of the iceberg called fatty liver. Children of diabetic patients are also prone to fatty liver, even if they are not obese. Hence, by diagnosing and taking timely advice, these dire long-term consequences can be prevented.
Fatty Liver Symptoms
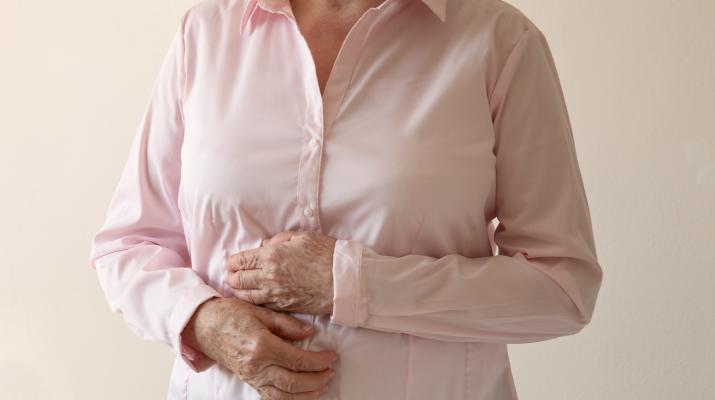
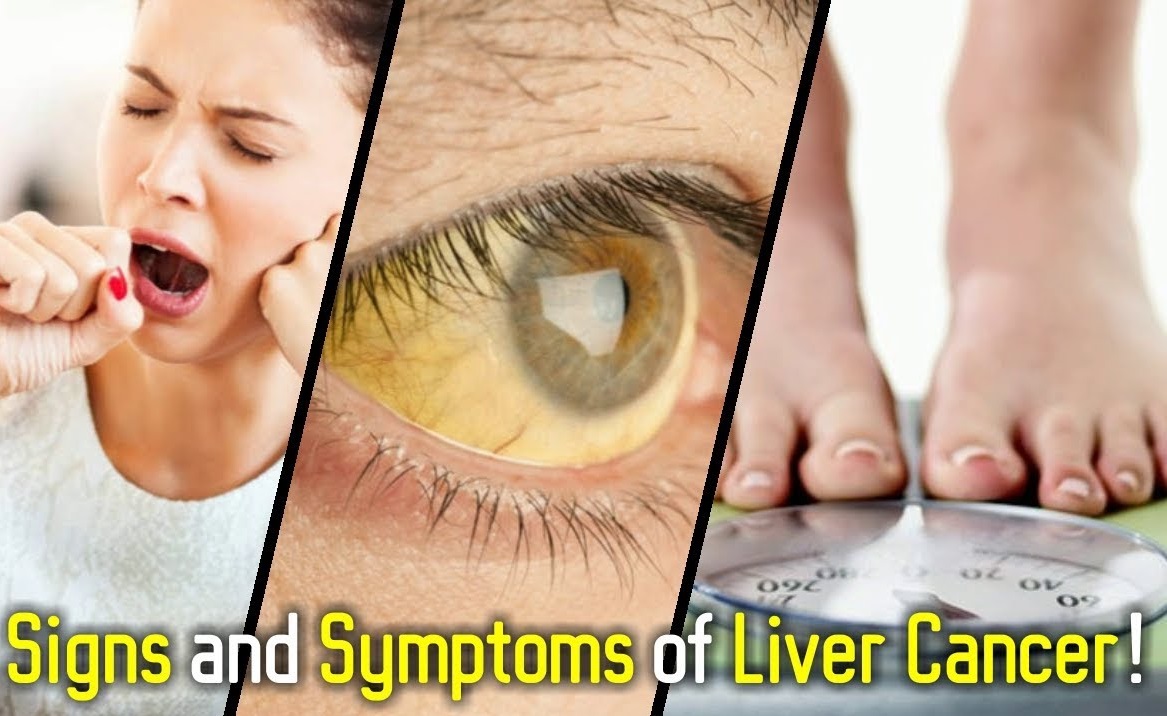
Most patients present with some heaviness in the right upper part of the abdomen or some kind of pricking sensation intermittently. Many can have a gaseous bloating sensation with indigestion or irregular bowel habits. Ladies having irregular menstrual periods and diagnosed with polycystic ovarian disease can also have fatty liver. Diabetic patients with poorly controlled sugars can have fatty liver, which worsens insulin resistance. Patients with advanced damage can present with jaundice, water in belly (called ascites) or vomiting of blood, which are features of end-stage cirrhosis.
fatty liver diagnosis
Fatty liver can be diagnosed by blood tests and ultrasound. Liver biopsy is the gold standard but not always required. Newer modalities like MR elastography are available, which can non-invasively give information on the stage of liver damage due to fat. Both are non-invasive. One should also do sugars and measure insulin resistance to check for pre-diabetes. ECG and lipid profile are recommended to check for heart condition. Hence, fatty liver and its consequences need to be assessed to ensure a comprehensive approach is adopted for a secure future.
Fatty Liver Treatment
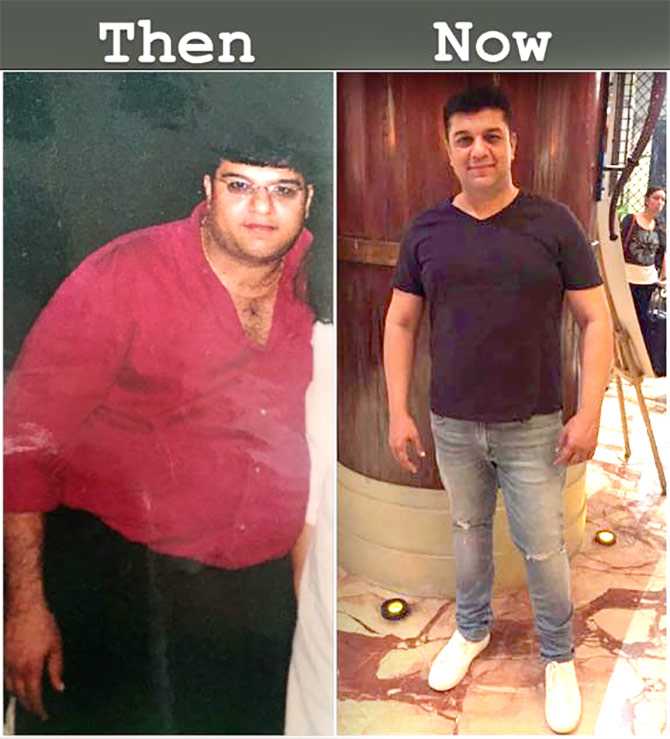
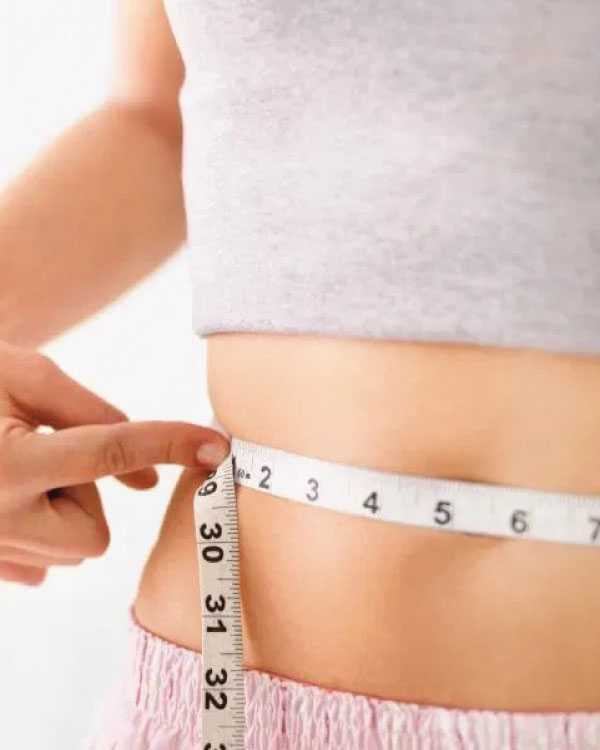
Treatment of fatty liver in the early stage can help in reducing the incidence of diabetes, heart problems, cholesterol and definitely advanced liver damage. Since prevention is better than cure, the best way is to screen for fatty liver in a young population with a family history of diabetes, heart problems or cirrhosis. If the damage is detected at an early stage, it is possible to halt the progression and reverse it to a normal healthy liver, as the liver has the capacity to regenerate.
A three-pronged strategy must be adopted for the treatment of fatty liver. The first and most vital arm of treatment is diet restriction and healthy lifestyle modifications, with consistent weight reduction. This will reduce the fat content in the liver. The key focus must be on adopting a low carbohydrate diet with small frequent meals and early dinner, preferably before 8 pm, so that overnight fasting is ensured. This remarkably helps in good sugar control and weight reduction.
Bariatric surgical options can be explored in patients with morbid obesity and advanced fatty liver damage with progressively worsening insulin resistance who have not responded positively to diet and lifestyle modifications.
Medical management is mainly focused on reversing the damage due to fat in the liver. There are a variety of drugs, which are used in the treatment of fatty liver. The dose and duration of the treatment are dependent on the stage of damage in the liver.
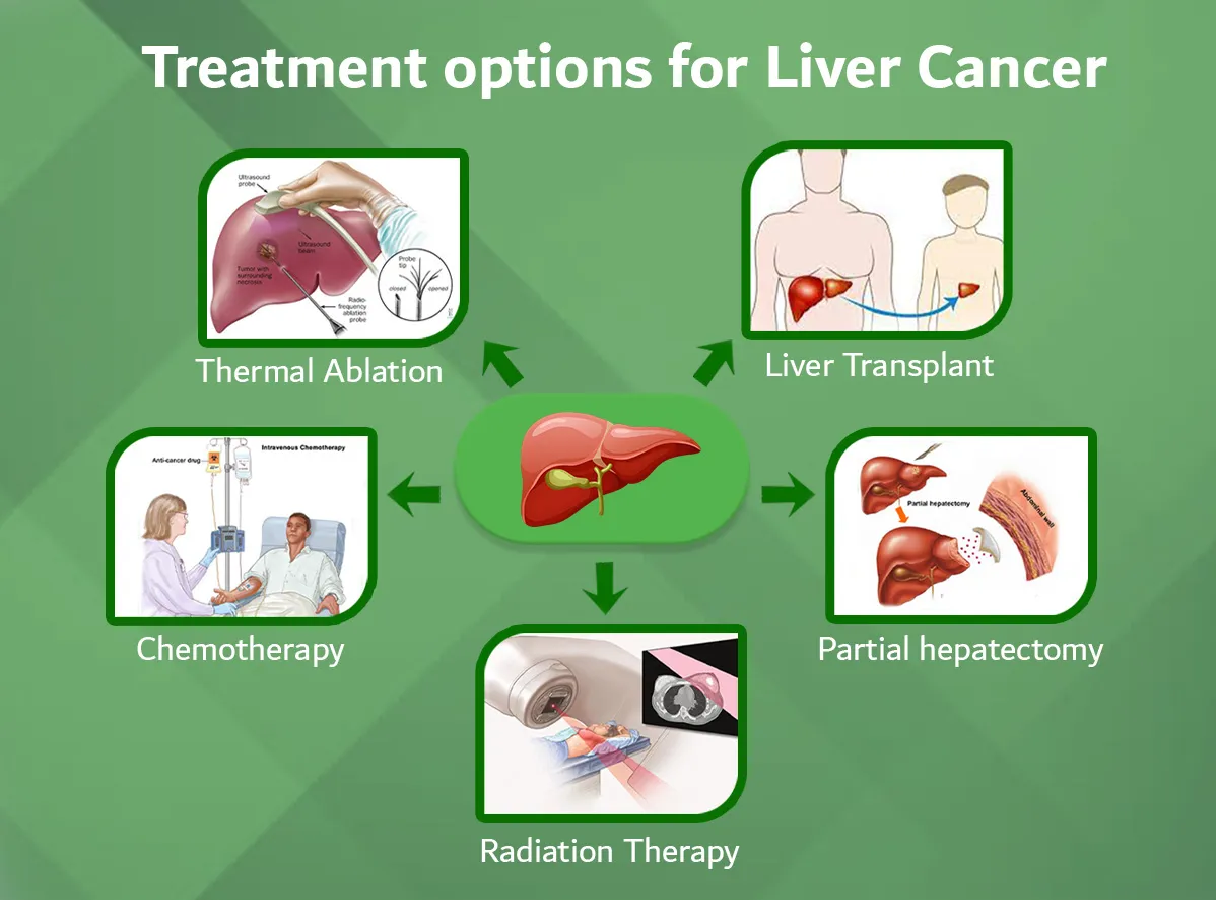
However, once the stage of fatty liver induced damage has progressed to end-stage cirrhosis, in most cases, the condition is not reversible. Hence, these patients should be on liver supportive medicines and be considered for timely liver transplantation as a long term definitive curative option. Once the liver functions start deteriorating, it can lead to life-threatening complications or develop into liver cancer.
For any health related query, connect with our experts by clicking below-
Reference
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21191681/
- https://www.nhp.gov.in/disease/non-communicable-disease/nonalcoholic-fatty-liver-disease-nafld
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30335697/
- https://main.mohfw.gov.in/newshighlights-42
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/nafld-nash/definition-facts
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24772746/