Health, Vitamin B12, Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Fatigue, Irritability, Inflammation- Signs & Symptoms you might have Vitamin B12 deficiency
Your body has several ways to show you if it is lacking any nutrient or is undergoing any illness. Symptoms like fatigue, irritability or inflammation may be a sign that your body is not getting enough nutrients.

Overview
While the importance of Vitamins like A and D are known, there is another important vitamin whose importance is still not well known and its deficiency is mostly neglected. Vitamin B12 deficiency is becoming common in people of all age groups, especially teenagers. It is essential to note that insufficient vitamin B12 levels can cause various serious complications such as anemia, low-grade inflammation, fatigue, tiredness, cognitive health problems, difficulty in walking, numbness, or tingling in the hands, legs, or feet.
Hence, it is imperative to monitor ones vitamin B 12 levels at regular intervals to check if it is in the normal and recommended range of 200 to 900 picograms per milliliter (pg/mL). (Source)
Vitamin B12 deficiency is one of the most neglected problems. One can become low on vitamin B12 when the body does not absorb or store enough of the vitamin, or one doesn’t get enough amount of it.
Vitamin B12 importance
Vitamin B12 is needed to form red blood cells and DNA. It is also a key player in the function and development of brain and nerve cells.
Recommended Intake Amount of Vitamin B12
The Recommended Dietary Allowance for men and women ages 14 years and older is 2.4 micrograms (mcg) daily. For pregnancy and lactation, the amount increases to 2.6 mcg and 2.8 mcg daily, respectively.
A Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) is the maximum daily dose unlikely to cause adverse side effects in the general population. No upper limit has been set for vitamin B12, as there is no established toxic level. However, some evidence suggests that supplements of 25 mcg per day or higher may increase the risk of bone fractures. (Source)
Vitamin B12 Deficiency Signs and symptoms
Sensations like numbness or tingling in the hands, feet, or legs, inability to walk, anemia, inflamed tongue, inflammation in the body, cognitive health problems, fatigue, irritability, poor appetite, low muscle tone, depression, vomiting, diarrhea, hyperpigmentation, seizures, delayed growth, poor motor development, and tiredness.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency Causes
1. Pernicious anaemia
Pernicious anaemia is an autoimmune condition that affects your stomach.
An autoimmune condition means your immune system, the body's natural defence system that protects against illness and infection, attacks your body's healthy cells.
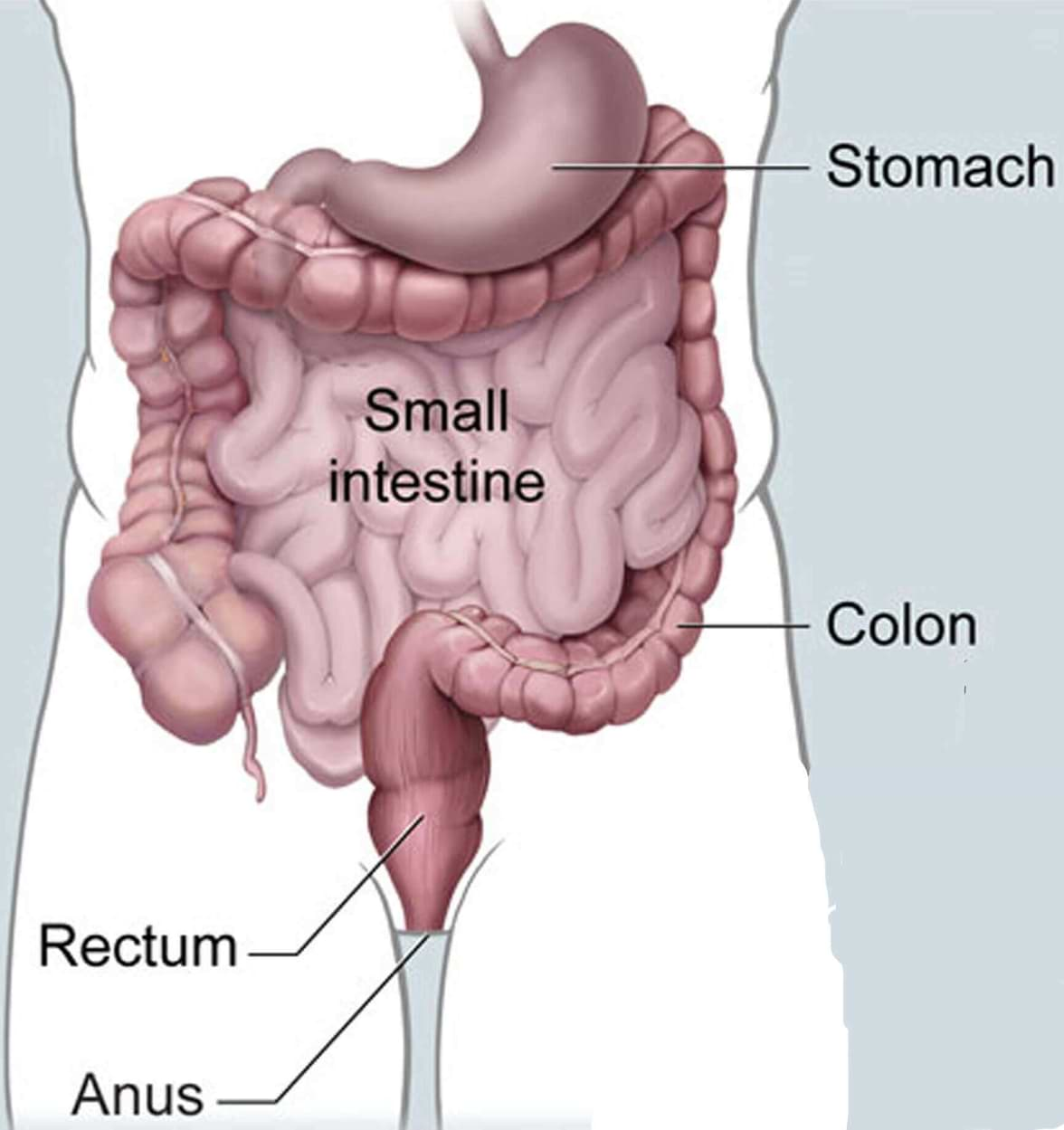
Vitamin B12 is combined with a protein called intrinsic factor in your stomach. This mix of vitamin B12 and intrinsic factor is then absorbed into the body in part of the gut called the distal ileum.
Pernicious anaemia causes your immune system to attack the cells in your stomach that produce the intrinsic factor, which means your body is unable to absorb vitamin B12.
The exact cause of pernicious anaemia is unknown, but it's more common in women around 60 years of age, people with a family history of the condition and those with another autoimmune condition, such as Addison's disease (a disorder in which the adrenal glands don't produce enough hormones) or vitiligo( a long-term condition where pale white patches develop on the skin caused by lack of melanin).
2. Diet
Some people can develop a vitamin B12 deficiency as a result of not getting enough vitamin B12 from their diet.
A diet that includes meat, fish and dairy products usually provides enough vitamin B12, but people who do not regularly eat these foods can become deficient.
People who eat a vegan diet and do not take vitamin B12 supplements or eat foods fortified with vitamin B12, are also at risk.
Stores of vitamin B12 in the body can last around 2 to 4 years without being replenished, so it can take a long time for any problems to develop after a dietary change.
3. Conditions affecting the stomach
Some stomach conditions or stomach operations can prevent the absorption of enough vitamin B12.
For example, a gastrectomy, a surgical procedure where part of your stomach is removed, increases your risk of developing a vitamin B12 deficiency.
4. Conditions affecting the intestines
Some conditions that affect your intestines can also stop you absorbing the necessary amount of vitamin B12.
For example, Crohn's disease https://obesitydoctor.in/disease/Crohns-Disease , a long-term condition that causes inflammation of the lining of the digestive system, can sometimes mean your body does not get enough vitamin B12.
5. Medicines
Some types of medicine can lead to a reduction in the amount of vitamin B12 in your body.
For example, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), a medicine sometimes used to treat indigestion, can make a vitamin B12 deficiency worse.
PPIs inhibit the production of stomach acid, which is needed to release vitamin B12 from the food you eat.
Your doctor will be aware of medicines that can affect your vitamin B12 levels and will monitor you if necessary.
6. Functional vitamin B12 deficiency
Some people can experience problems related to a vitamin B12 deficiency, despite appearing to have normal levels of vitamin B12 in their blood.
This can happen as the result of a problem known as functional vitamin B12 deficiency, where there's a problem with the proteins that help transport vitamin B12 between cells.
This results in neurological complications involving the spinal cord.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency Diagnosis & Treatment
If you are feeling any of the symptoms, consult the doctor without any delay. They will advise you to take a test to ascertain your B12 level. You will be suggested to take B12 in the form of a supplement or injection. Your treating doctor will direct you regarding how much and how to take it .
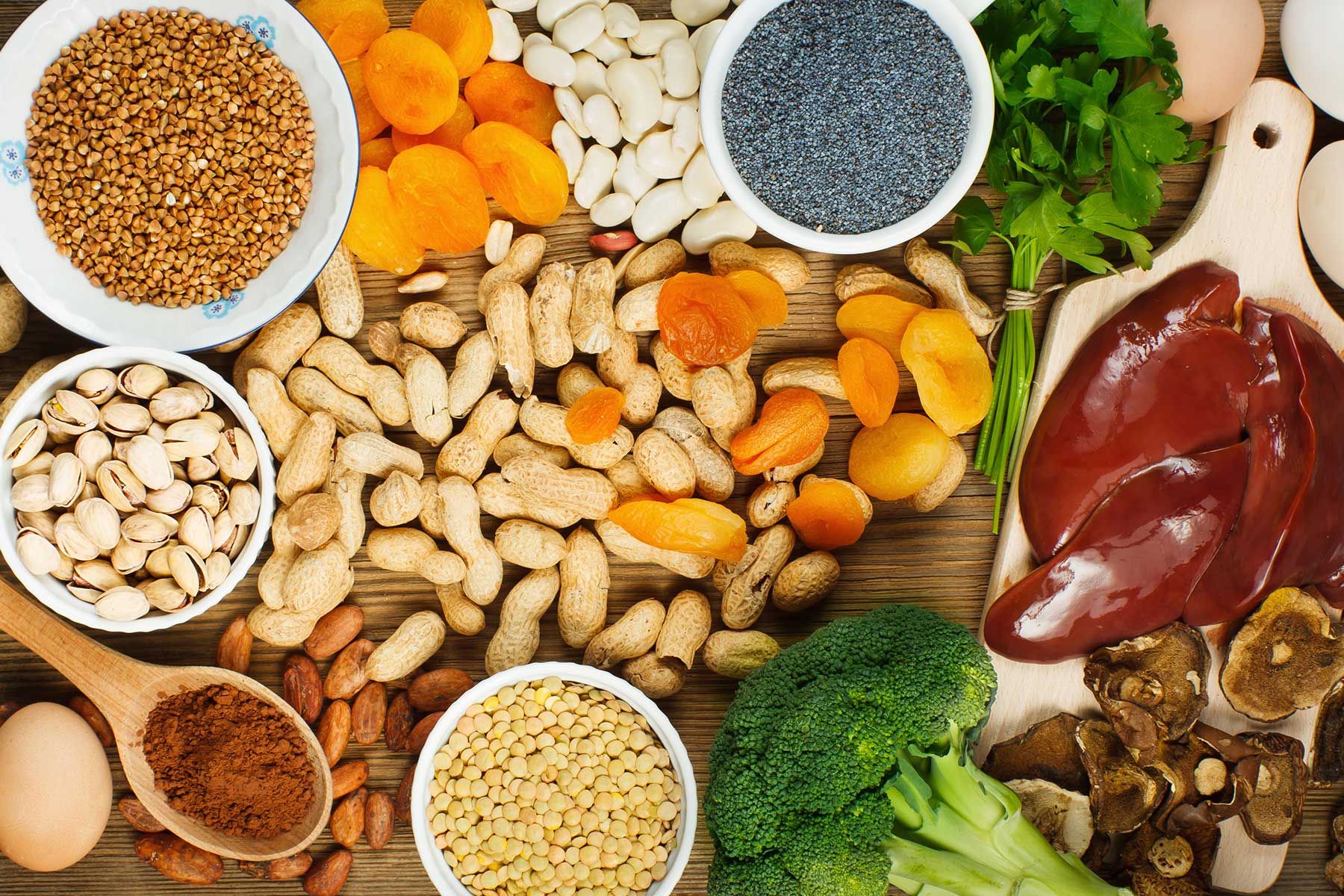
Sources of vitamin B 12
Dairy products, almonds, salmon, chicken, eggs, mackerel, tofu, mushrooms, and tuna have enough vitamin B12 and can be consumed after consulting an expert. But, also note that high levels of B12 can also be harmful to health. So, follow the instructions given by the doctor. (Source)
Word from us
Vitamin B12 deficiency can affect any individual at any period of time however timely detection of B12 deficiency and prompt treatment can help you to avoid severe complications like neurologic issues and blood disease. Especially for kids and teenagers in their growing age, the right level of nutrients is important for improving their growth and development.
Reference
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB12-HealthProfessional/
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vitamins-and-minerals/vitamin-b/
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vitamin-b12-or-folate-deficiency-anaemia/causes/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2781043/
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/vitamin-b12/